STM32 Boot Modes
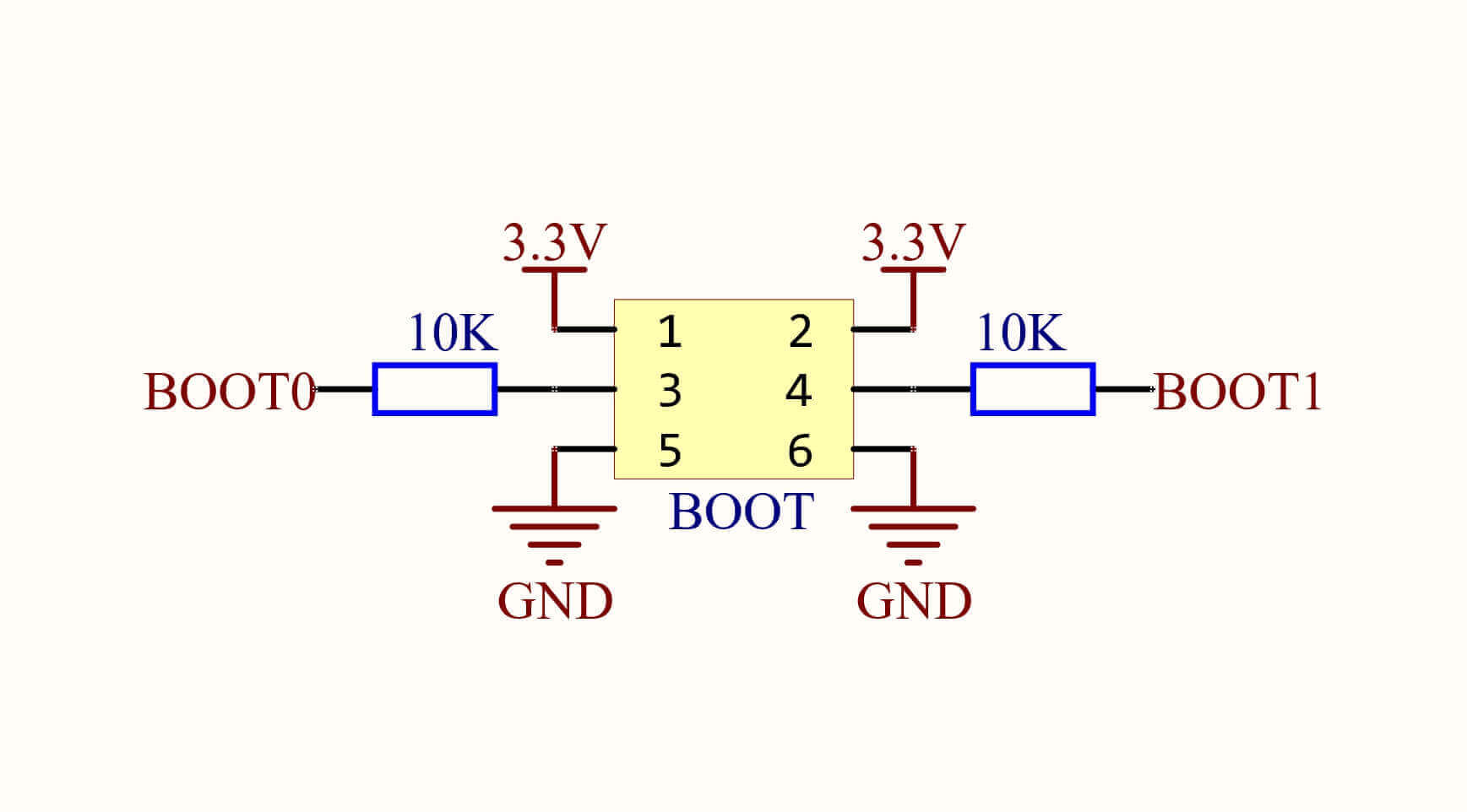
The STM32 microcontroller offers the flexibility of choosing the startup mode by configuring the BOOT1 and BOOT0 pins. These pins determine the boot behavior of the microcontroller upon power-on or reset.
Here are the three available startup modes:
1. Boot from Main Flash Memory
| BOOT0 | BOOT1 |
|---|---|
| Low | Any |
In this mode, the microcontroller starts up from the onboard Flash memory. This is the typical configuration for normal operation when using Flash memory with sizes of 64K, 128K, or 256K.
2. Boot from System Memory
| BOOT0 | BOOT1 |
|---|---|
| High | Low |
This mode is used when downloading firmware via serial communication (e.g., UART) or in-system programming (ISP). It allows for programming and debugging of the microcontroller.
3. Boot from Internal SRAM
| BOOT0 | BOOT1 |
|---|---|
| High | High |
Starting from internal SRAM serves two primary purposes:
- It enhances efficiency during repetitive firmware downloads and debugging processes because downloading to Flash memory is relatively slower. However, it's important to note that power loss will result in the loss of the program.
- It is used for disabling read protection and erasing the Flash memory to restore it to its factory state.
Additional Information
In the tables above, "High" and "Low" indicate the states when the pins are connected to a 10KΩ pull-up or pull-down resistor, rather than directly connected to VCC or GND.
References and Acknowledgments
Original: https://wiki-power.com/ This post is protected by CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 agreement, should be reproduced with attribution.
This post is translated using ChatGPT, please feedback if any omissions.