RobotCtrl - STM32 Universal Development Kit
Project Repository: linyuxuanlin/RobotCtrl
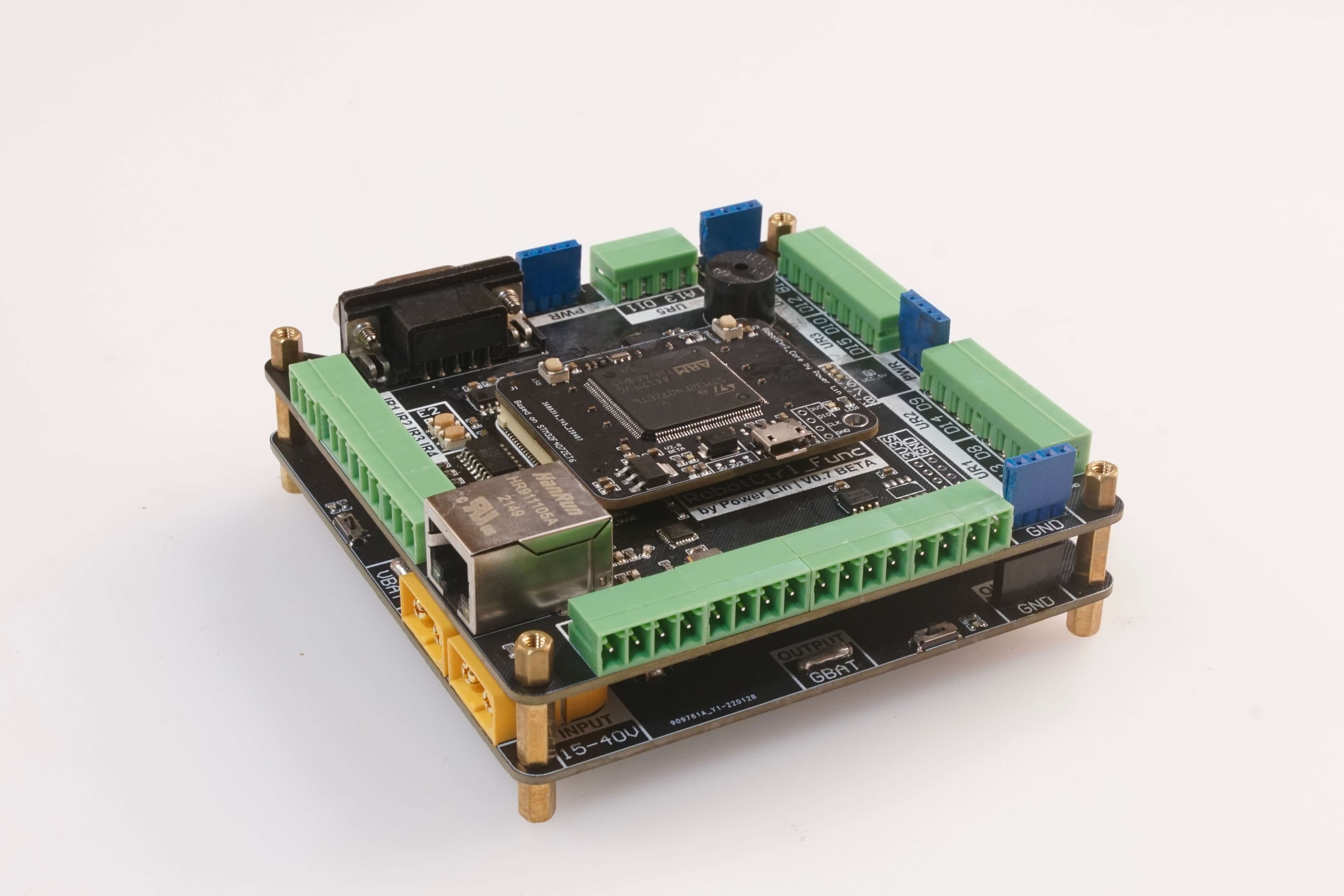
RobotCtrl - STM32 Universal Development Kit consists of three boards:
- RobotCtrl_Core - Core Board
- RobotCtrl_Func - Peripheral Expansion Board
- RobotCtrl_Power - Power Supply Board
Design Requirements
Note: The following is a design summary. For specific details, please refer to the respective articles.
Design Approach for RobotCtrl_Core
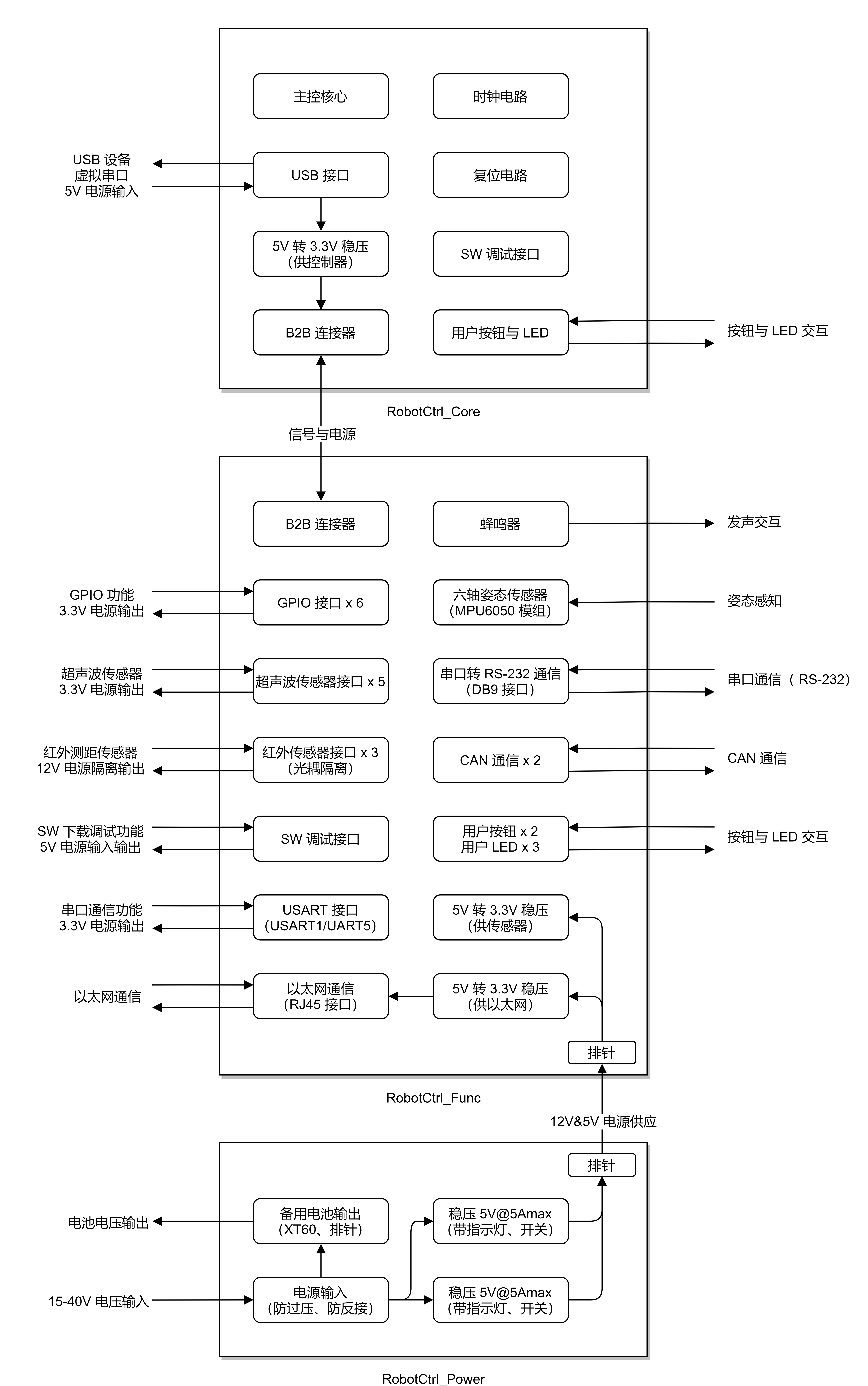
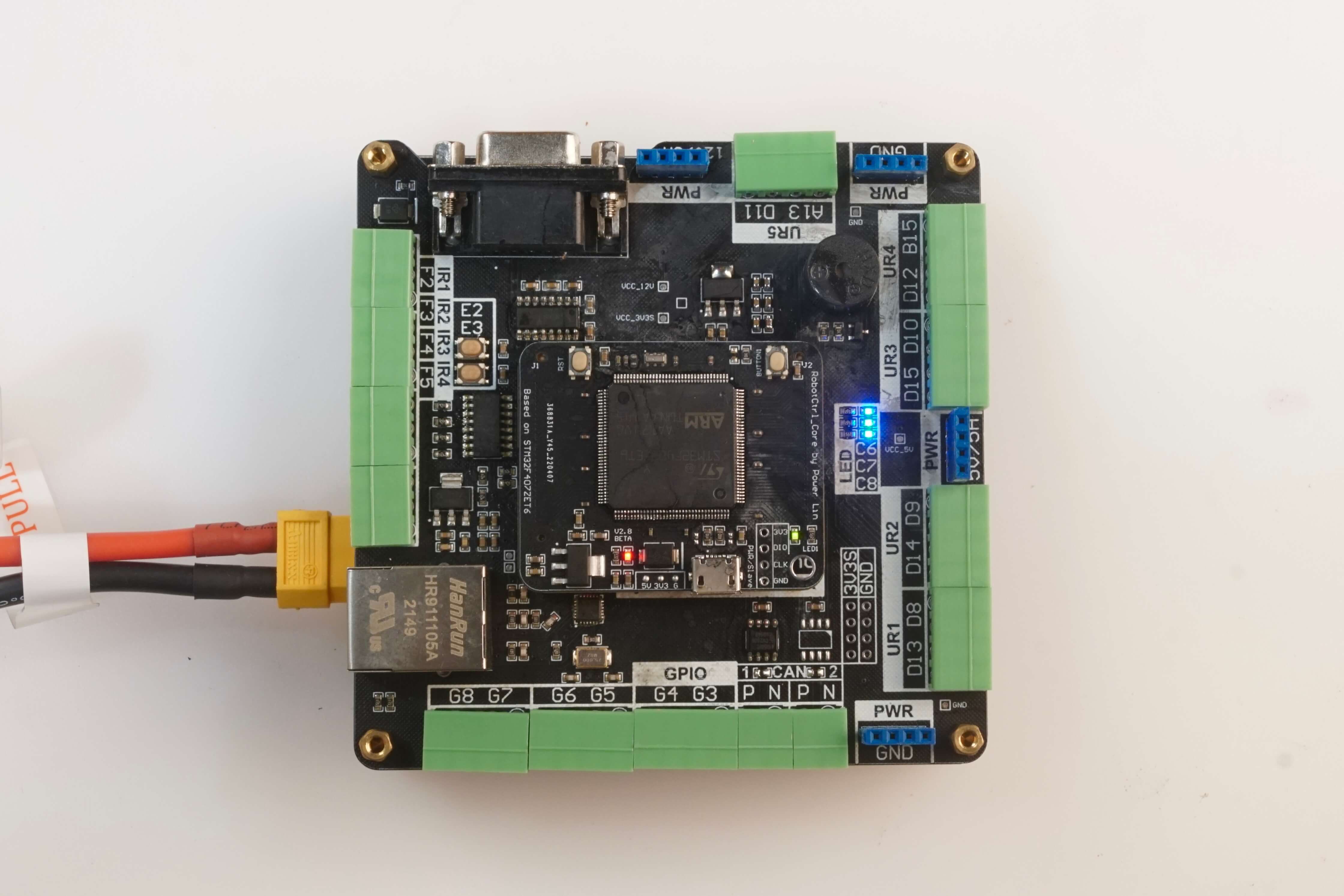
The schematic design for RobotCtrl_Core includes the power supply circuit, microcontroller minimum system, USB communication, B2B connector, user buttons, and LED components.
The power supply circuit uses an LDO, known for its advantages of simplicity, low output ripple, cost-effectiveness, and a small layout area. With the addition of appropriate decoupling capacitors and power indicator LEDs, it regulates the 5V input voltage from the USB port or B2B connector to a stable 3.3V (with a maximum current of 1A).
In the minimum system design, the power source is a 3.3V input with corresponding decoupling capacitors. Additionally, a dedicated ADC power supply (VDDA) is connected to VDD through a 120Ω ferrite bead, with additional decoupling capacitors. The reset circuit includes an external button to trigger a low-level NRST pin to reset the system. The clock circuit adds an external high-speed HSE clock, with an external passive crystal oscillator connected to OSC_IN and OSC_OUT pins. The default boot mode is set to boot from the on-chip Flash memory, with BOOT0 set low and BOOT1 set to any level, using a 10k resistor to pull BOOT0 to ground. The download and debug circuit directly exposes the SW interface (DIO/CLK).
For the USB communication circuit, the STM32F4 has a built-in USB peripheral. An external USB Micro connector is used, with series resistors of 10Ω on the data lines and TVS and ESD diodes on both the signal and power lines to meet EMC requirements.
The B2B connector is used for power supply and data communication between RobotCtrl_Core and RobotCtrl_Func. In this design, two B2B connectors are sufficient to expose all the I/O pins of the STM32F407ZE microcontroller, enhancing expandability in the future.
Design Approach for RobotCtrl_Func
The schematic design for RobotCtrl_Func primarily includes serial communication (RS-232/TTL), CAN communication, Ethernet communication, attitude sensors, ultrasonic interfaces, infrared distance measurement interfaces (with optocoupler isolation), buzzer, SW download and debug interface, user buttons and LEDs, general GPIO interfaces, power supply, and B2B connectors, among other modules.
The serial communication circuit provides TTL and RS-232 level interfaces. Specifically, TTL directly connects to the TX/RX pins of USART1 and UART5, while the RS-232 communication circuit uses a TTL-to-232 level converter chip to convert the microcontroller's TTL to RS-232 level. To improve EMC performance, the DB9 connector's outer shell pins can be connected to TVS diodes grounded, and the TTL-to-232 chip requires additional power decoupling and bootstrap capacitors.
The CAN communication circuit is based on CAN transceiver chips and utilizes differential voltage transmission for the CAN bus. 120Ω termination resistors are added to the CAN bus to match impedance and reduce signal reflections.
Ethernet communication is based on an Ethernet PHY chip, which communicates with a microcontroller through an RMII interface and communicates over an external network cable connected to an RJ45 port with built-in isolation transformers. The Ethernet circuit's clock utilizes an external 25MHz passive crystal oscillator and requires independent power to reduce power interference. Here, the same low-dropout linear regulator scheme as the core board is used to supply power to the Ethernet circuit separately.
The circuit for the four-channel infrared ranging sensor interface is designed to accommodate the 12V power supply and signal (NPN normally open type) used by the infrared sensors. It draws power from RobotCtrl_Power through a 12V output and includes four optocoupler isolation chips to transmit high and low-level signals. The design of the optocoupler isolation circuit requires determining the resistance value of the current-limiting resistor based on the current's magnitude to ensure it falls within the trigger voltage range specified in the data sheet. The attitude sensor module design incorporates an MPU6050 module and reserves an I2C interface for communication with the microcontroller.
Design Philosophy of RobotCtrl_Power
The schematic design of RobotCtrl_Power mainly consists of XT60 dual power inputs, a 24V to 12V conversion, a 24V to 5V voltage regulation circuit, as well as enable switches, power indicator lights, reverse connection protection, overvoltage protection circuits, and other components.
Two XT60 connectors are used for power input, where one terminal is for the main power input, and the other terminal can be used for an auxiliary power source or as a battery power output for external use.
The reverse connection protection circuit utilizes a MOSFET-based design. Under normal power connection, the MOSFET is in the conducting state, and in the case of reverse connection, it goes into cutoff, thus protecting the circuit. In this design, a domestically produced P-MOSFET is used for reverse connection protection, and a voltage divider and voltage-locking diode are employed to set the gate threshold voltage for forward conduction. To achieve overvoltage and ESD protection, TVS diodes are connected in parallel at the power input.
The design of the 12V/5V voltage regulation circuit adopts a Buck non-isolated switching voltage regulation solution based on the LMR14050. Based on the principles of the Buck topology and the reference from the voltage regulator chip's datasheet, resistor values for feedback are chosen to maintain the output at 12V/5V. When selecting the inductance component, it's important to ensure that the maximum saturation current is greater than the ripple current and leaves sufficient margin. A Schottky diode is chosen for high-speed switching, and its voltage and current must meet the circuit's requirements. Additionally, both input and output require parallel decoupling capacitors to filter out ripple.
The enable switch controls the activation and deactivation of the voltage regulation output, and the enable pin of the Buck chip is connected to achieve soft start and shutdown of the voltage regulation output. The power indicator lights inform the user about the status of the 12V/5V regulated output.
References and Acknowledgments
This project is my personal graduation design. During the design, soldering, and debugging of the project, I encountered various challenges of all sizes. With the strong support of my advisor, colleagues, and friends, I was able to successfully overcome these challenges and achieve the honor of an outstanding graduation project. Thank you!
Original: https://wiki-power.com/ This post is protected by CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 agreement, should be reproduced with attribution.
This post is translated using ChatGPT, please feedback if any omissions.