HAL Library Development Notes - Serial Communication
This article is based on the in-house RobotCtrl development kit, with the microcontroller core being the STM32F407ZET6 and RS-232 communication utilizing the SP3232EEN chip. For schematic diagrams and a detailed introduction, please refer to RobotCtrl - STM32 Universal Development Kit.
Basic Principles
For the basic principles of serial communication, please refer to the article on Communication Protocol - Serial Communication.
Serial Communication Experiment
Before proceeding with the next experiment, you need to configure various parameters such as serial downloading and clock settings in CubeMX. For specific steps, please refer to the article HAL Library Development Notes - Environment Configuration.
Configuring Serial Ports in CubeMX
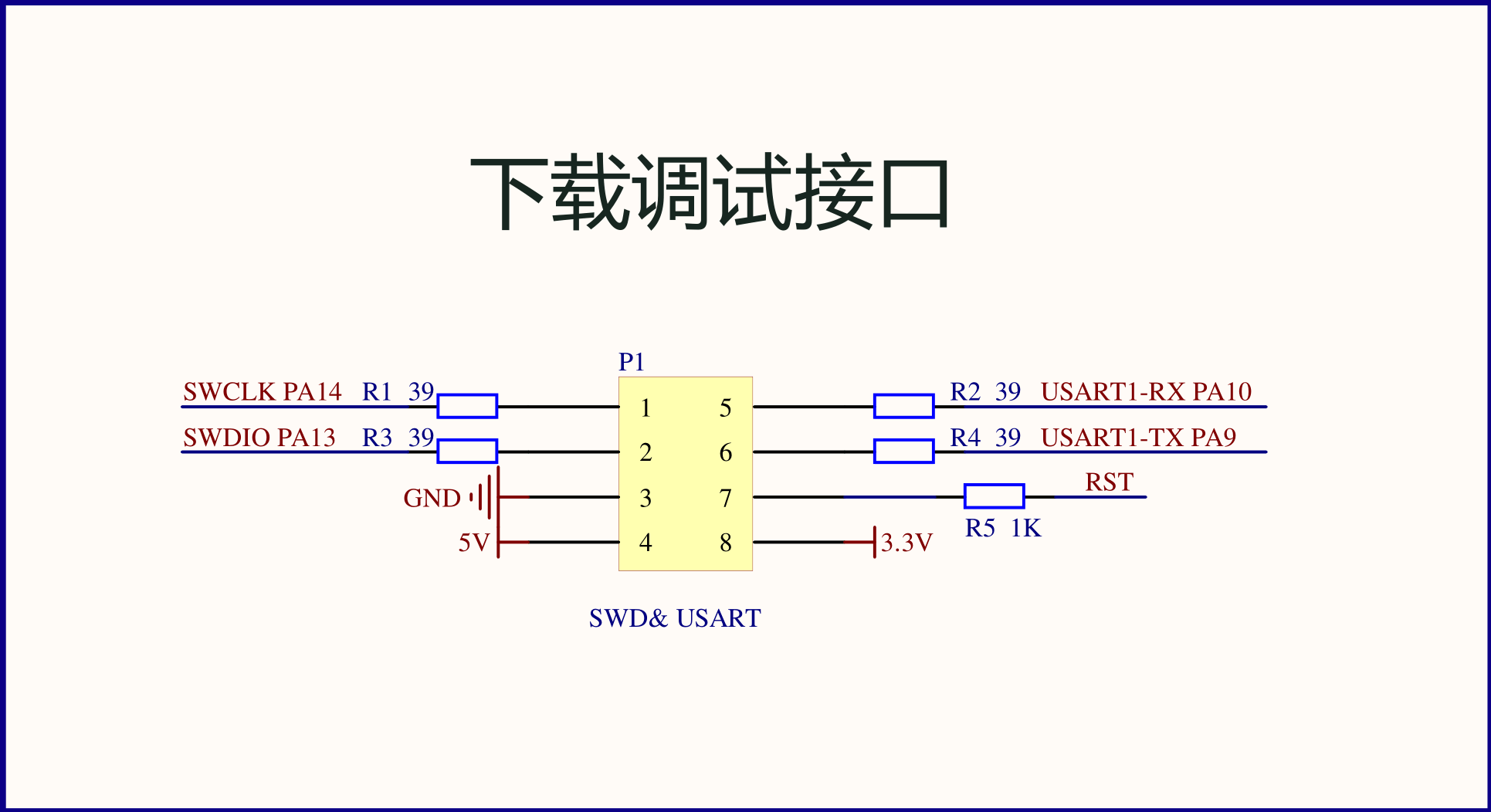
According to the schematic, the serial port we are using for communication experiments is USART1, which corresponds to the PA9 and PA10 pins. To configure these two pins as the transmit and receive functions of USART1 in CubeMX, navigate to the USART1 tab on the left, set the mode to asynchronous, and modify parameters such as baud rate as shown below:
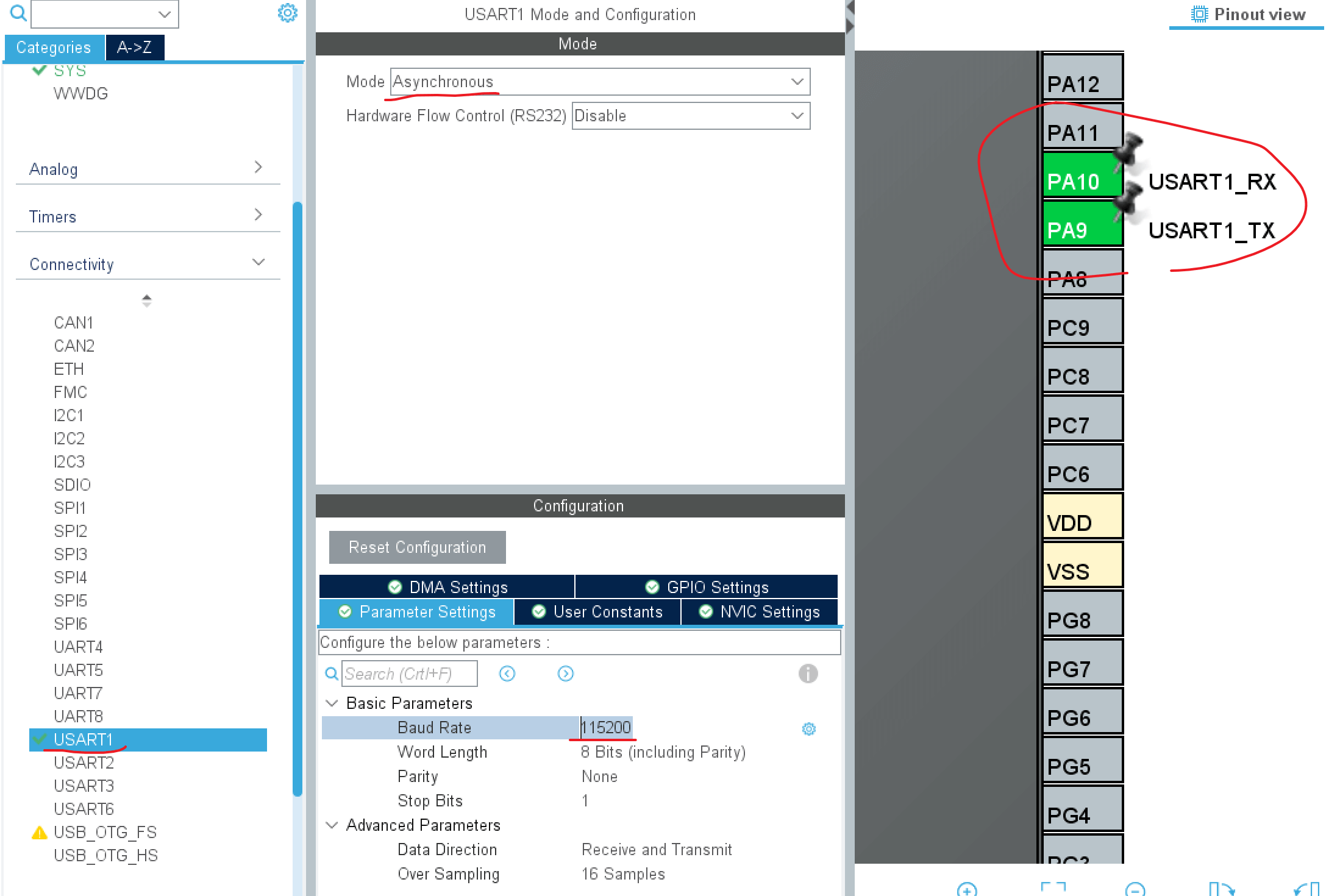
Here are the parameter details:
- Baud Rate Setting: There is no universally best baud rate; it should be modified based on the actual circumstances and match the settings in the serial debugging assistant.
- Data Word Length: If parity is enabled, the actual data will be one bit less than this value.
- Parity: You can choose between odd, even, or no parity.
- Stop Bits: One or two extra bits used as end-of-transmission or end-of-reception signals.
- Data Direction: You can choose between transmit-only, receive-only, or full-duplex modes.
- Over Sampling: Using an 8x or 16x oversampling rate can effectively prevent data errors.
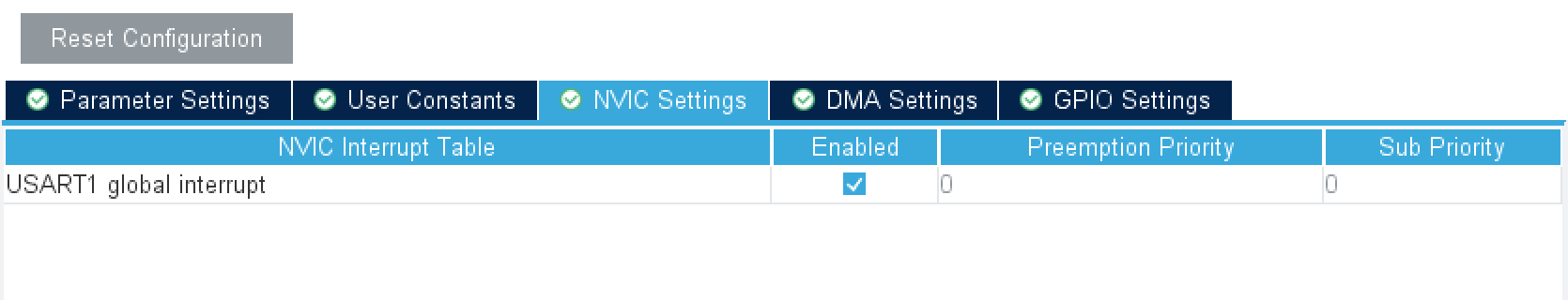
Finally, enable the USART1 serial port interrupt in the NVIC tab, as shown below:
Configuring Serial Ports in Code
First, you need to add the following code at the end of stm32f4xx_it.c:
/* USER CODE BEGIN 1 */
void HAL_UART_RxCpltCallback(UART_HandleTypeDef *huart)
{
if(huart->Instance==USART1)
{
HAL_UART_Receive_IT(huart, &aRxBuffer, 1); // Receive and write to aRxBuffer
HAL_UART_Transmit(huart, &aRxBuffer, 10, 0xFFFF); // Send back the received aRxBuffer
}
}
/* USER CODE END 1 */
Here, aRxBuffer is a uint8_t global variable defined in main.c. With this code, an interrupt is generated after receiving each byte, and the byte is returned and the interrupt is re-enabled. You need to define it in both main.c and stm32f4xx_it.c separately:
/* Private variables -----------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN PV */
uint8_t aTxBuffer[] = "USART TEST\r\n"; // String for sending
uint8_t aRxBuffer[20]; // String for receiving
/* USER CODE END PV */
/* Private variables -----------------------------------------------------------*/
/* USER CODE BEGIN PV */
extern uint8_t aTxBuffer;
extern uint8_t aRxBuffer;
/* USER CODE END PV */
In addition, in main.c, we need to enable the receive interrupt function after initializing the UART and before entering the main loop:
/* USER CODE BEGIN 2 */
HAL_UART_Receive_IT(&huart1, (uint8_t *)aRxBuffer, 1); // Enable receive interrupt
/* USER CODE END 2 */
You can also send an initialization message to indicate that the UART is up and running:
/* USER CODE BEGIN 2 */
HAL_UART_Transmit(&huart1, (uint8_t*) aTxBuffer, sizeof(aTxBuffer) - 1, 0xFFFF); // Send the previously defined aTxBuffer
/* USER CODE END 2 */
If you need to redirect printf (use the printf function for serial output in STM32), please refer to STM32CubeIDE Serial Redirection (printf) and Output of Floating-Point Numbers.
Download and Verification
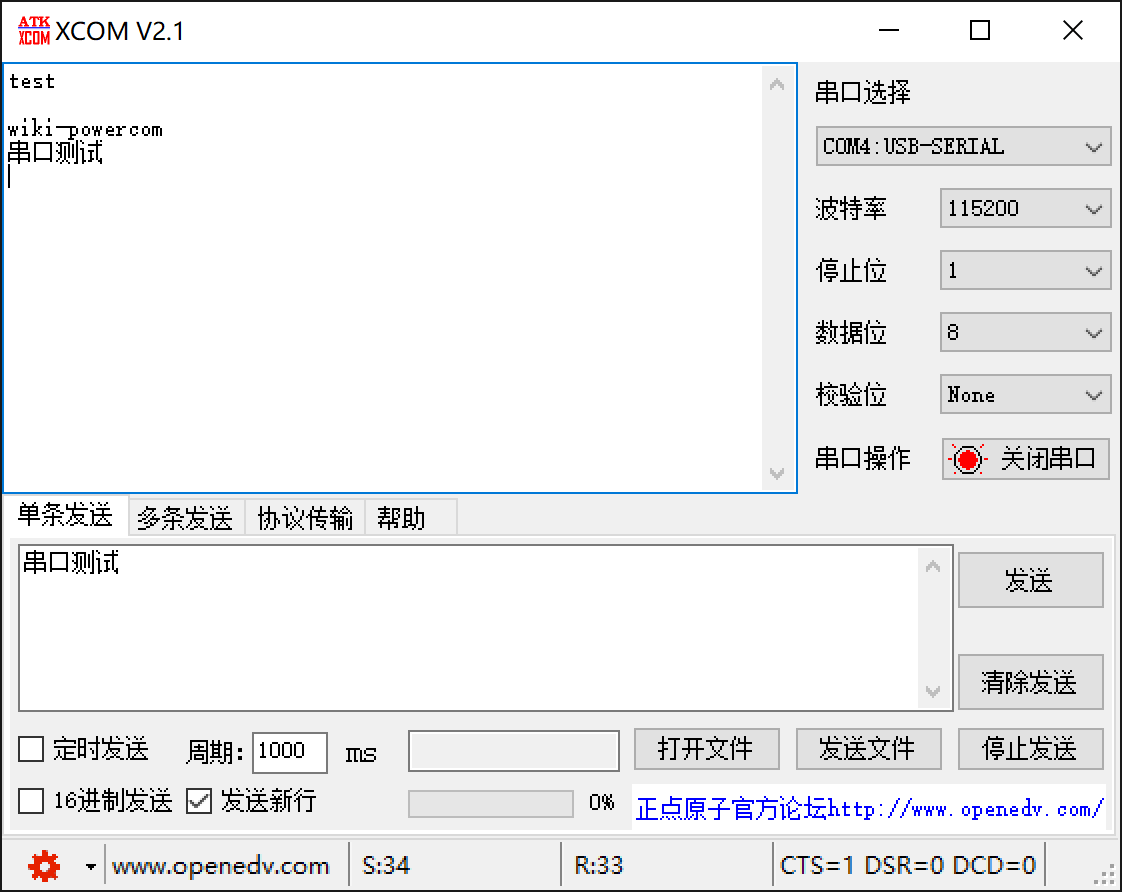
After successfully programming the application, open a serial terminal, configure the appropriate port and baud rate.
Once connected to the serial port, it will first print the contents of aTxBuffer, and then it will echo the received aRxBuffer. As shown below:
References and Acknowledgments
- STM32CubeMX Practical Tutorial (Part Six) - Serial Communication
- Advanced Part III [UART & USART]
- Non-Blocking HAL_UART_Receive_IT in STM32 Analysis and Practical Application
- HAL Library Tutorial 6: UART Data Reception
Original: https://wiki-power.com/ This post is protected by CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 agreement, should be reproduced with attribution.