Several Output Modes of Encoders
Open Collector (OC) Output
Open Collector, which means opening the collector of the transistor. Open Collector output uses the emitter of the output circuit transistor as the common terminal, and the collector is left floating. It is generally divided into NPN and PNP Open Collector.
NPN Open Collector:
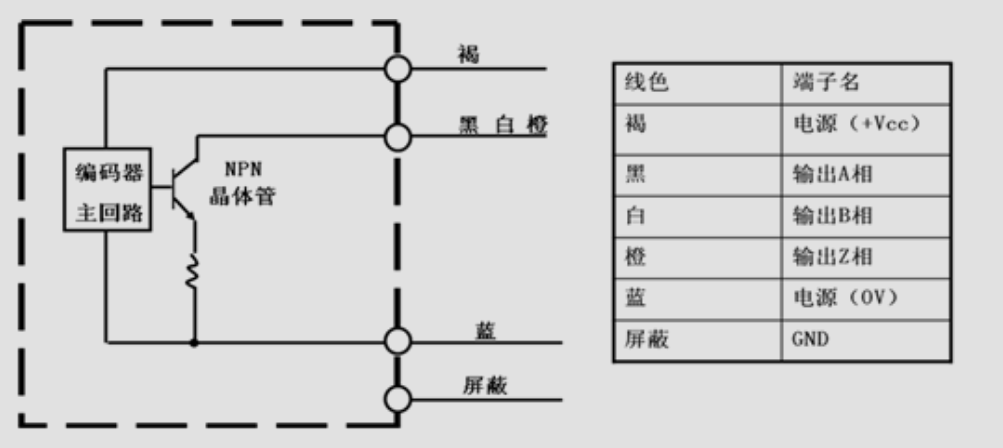
PNP Open Collector:
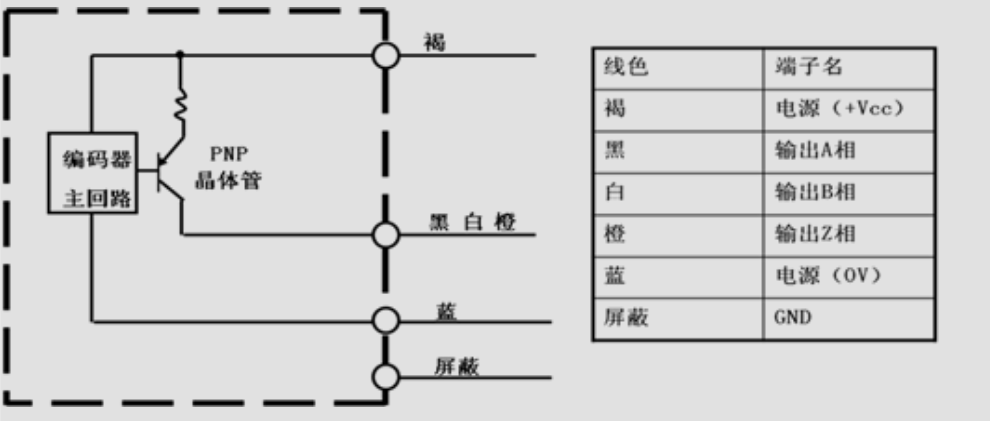
When using it, the signal pin needs to be pulled up to achieve the function of Open Collector output.
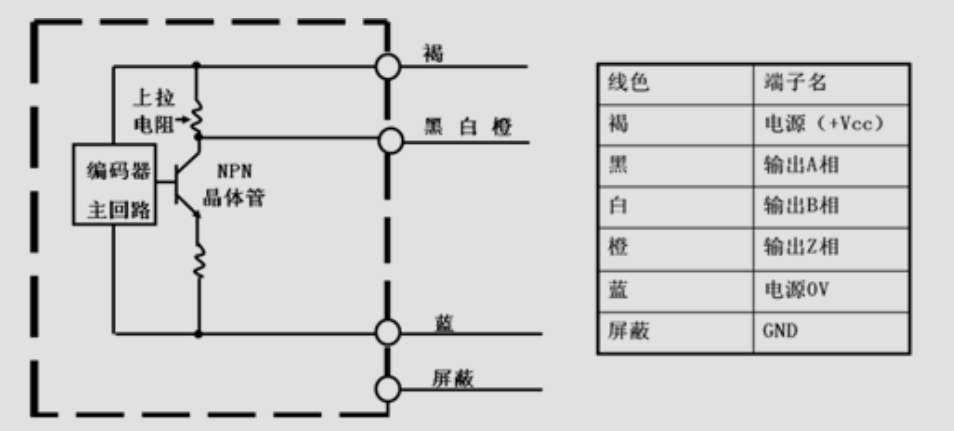
Voltage Output
Voltage Output is based on the open circuit output of the collector, with a pull-up resistor connected between the power supply and the collector, so that there can be a stable voltage state between the collector and the power supply. No pull-up resistor is needed when using it.
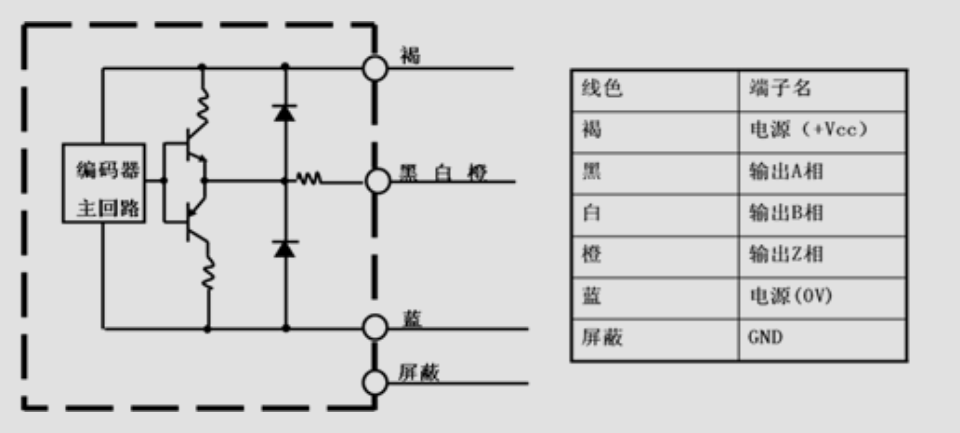
Complementary Output
Complementary Output is an output circuit that has both NPN and PNP output transistors. According to the high/low level of the output signal, the two output transistors interact to perform on/off actions. Compared with the open circuit output of the collector, the transmission distance of the circuit with complementary output can be slightly longer. It can also be connected to the collector open circuit input machine (NPN, PNP).
Linear Drive Output
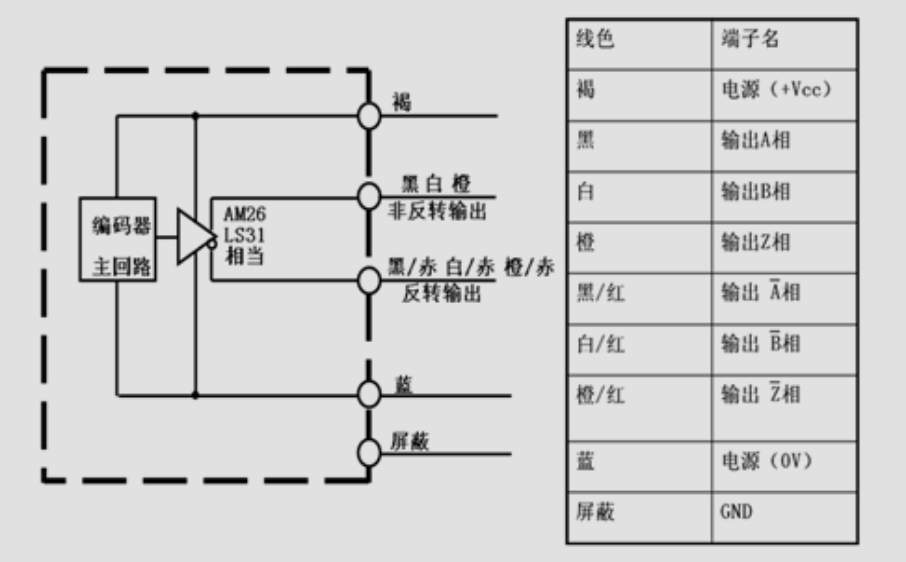
Linear Drive Output uses the RS-422 standard and applies the AM26LS31 chip to high-speed and long-distance data transmission. The signal is output in a differential form, so it has stronger anti-interference ability. The output signal can only be received by devices specifically designed to receive linear drive output.
References and Acknowledgements
Original: https://wiki-power.com/ This post is protected by CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 agreement, should be reproduced with attribution.
This post is translated using ChatGPT, please feedback if any omissions.