Radio Frequency - Radio Waves and Antennas 🚧
Radio Waves and Ultra Short Waves
The Concept of Radio Waves
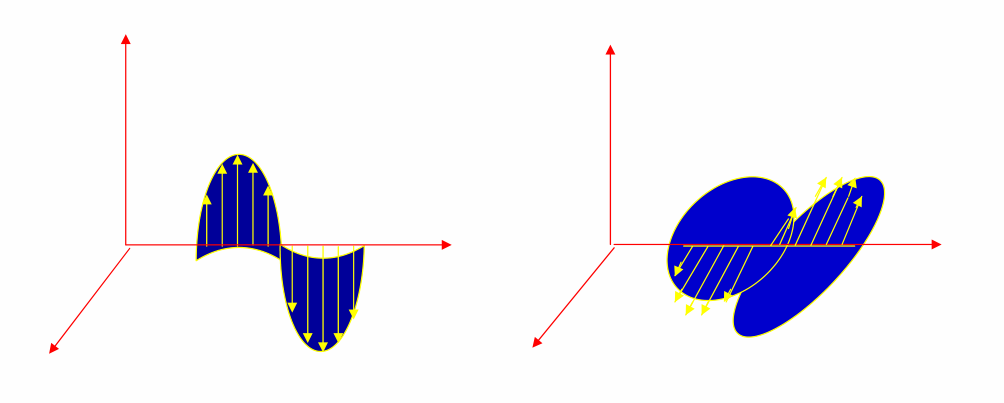
Radio waves are a form of energy transmission. During their propagation, electromagnetic waves are mutually perpendicular in space, simultaneously perpendicular to the direction of propagation.
Radio waves, like waves in a pond, weaken as they propagate.
The speed of radio wave propagation in a vacuum is equal to the speed of light (c, 300,000 km/s). In a non-vacuum environment, the propagation speed is influenced by the medium and is calculated with the following formula:
Here, \(\varepsilon\) represents the dielectric constant of the propagation medium.
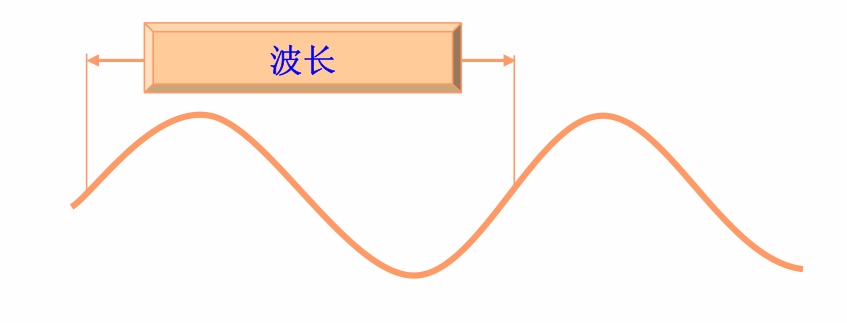
The relationship between the wavelength, frequency, and propagation speed of radio waves is as follows:
Where \(\lambda\) is the wavelength (m), \(V\) is the propagation speed (m/s), and \(f\) is the frequency (Hz).
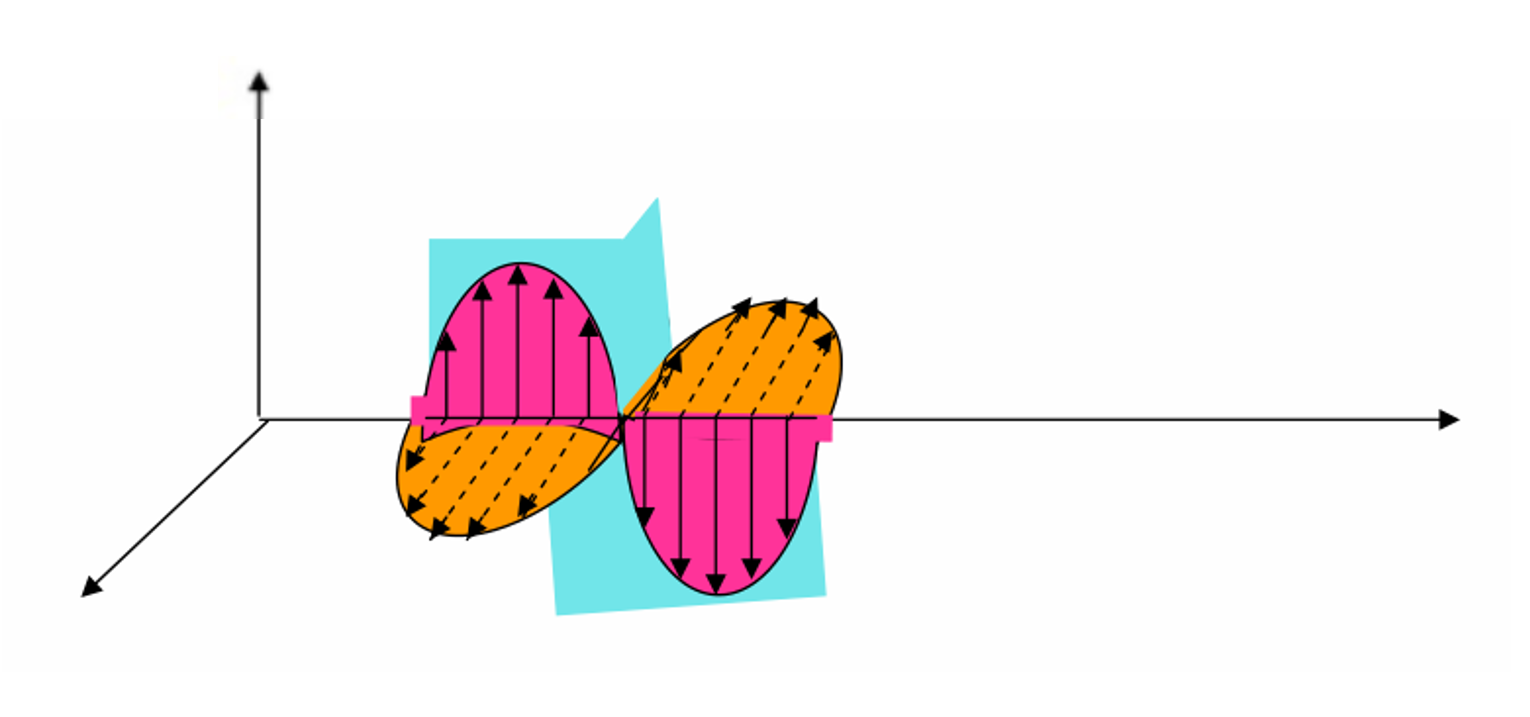
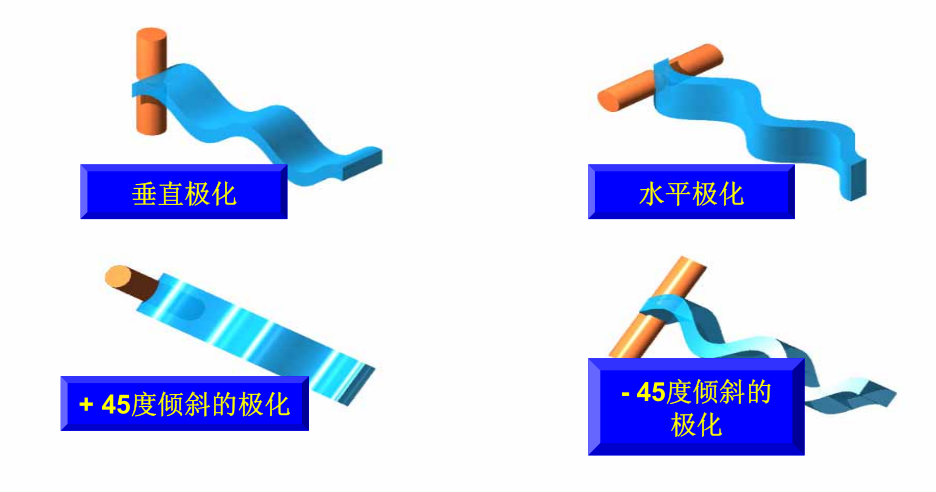
Polarization of Radio Waves
The polarization of radio waves refers to the systematic variation in the electric field direction of radio waves as they propagate in space.
Antennas
Polarization of Antennas
The electric field direction of the electromagnetic field radiated by an antenna is the polarization direction of the antenna.
Principles of Antennas
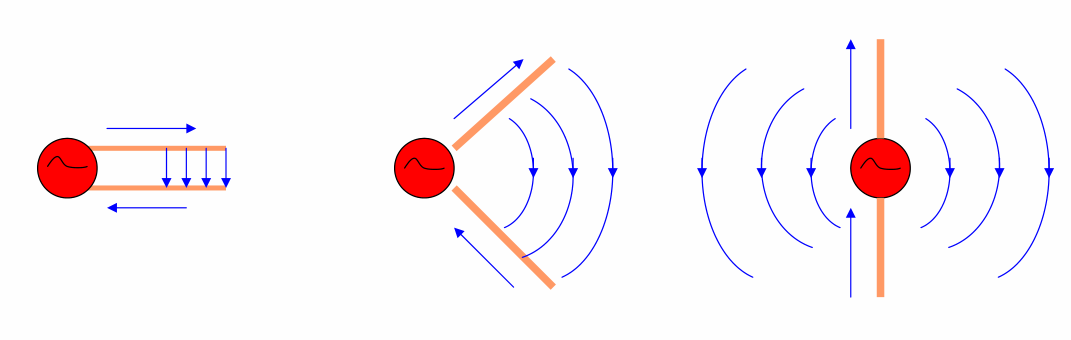
When a conductor carries alternating current, it can generate the radiation of electromagnetic waves, and this radiation capability is related to the length and shape of the conductor.
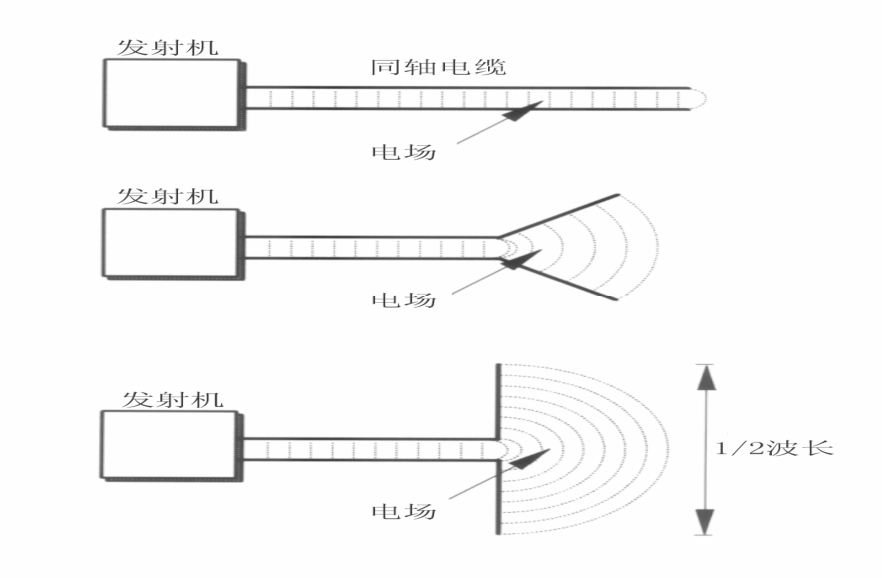
When the length of the conductor becomes comparable to the wavelength, the current on the conductor significantly increases, thereby creating stronger radiation. Conductor segments capable of producing significant radiation are typically referred to as "radiators."
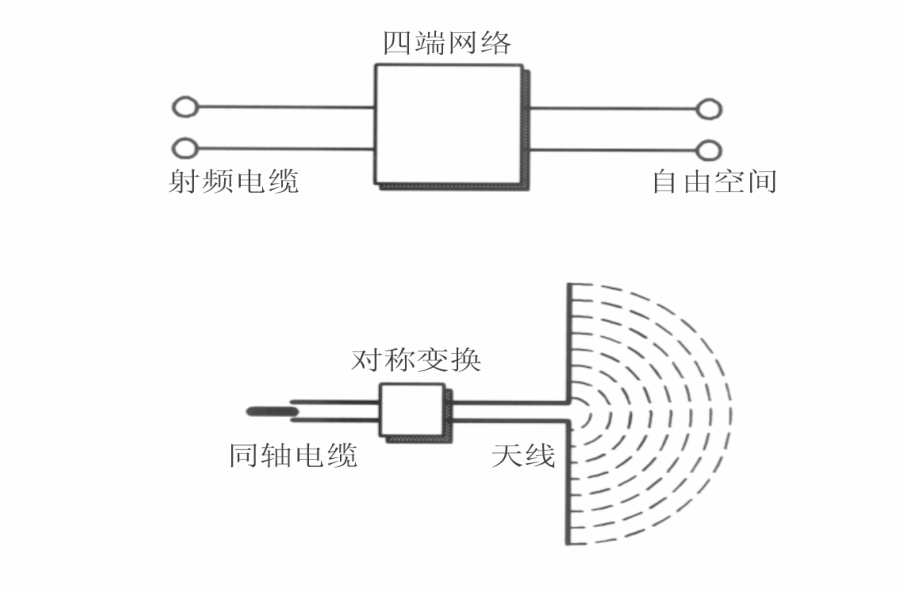
An antenna can be viewed as a four-terminal network:
If the lengths of the arms of the radiator are equal, it is known as a symmetric radiator or half-wave radiator:
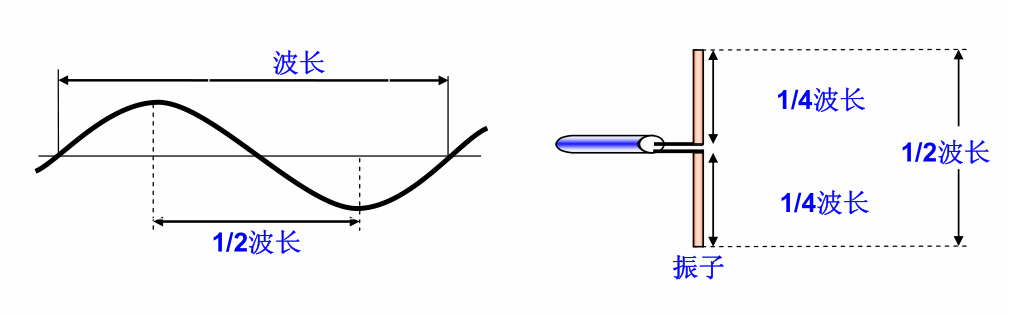
For instance, a 400MHz symmetric radiator has a length of approximately 400mm, while an 800MHz symmetric radiator has a length of about 200mm.
Various field distributions on a symmetric radiator:
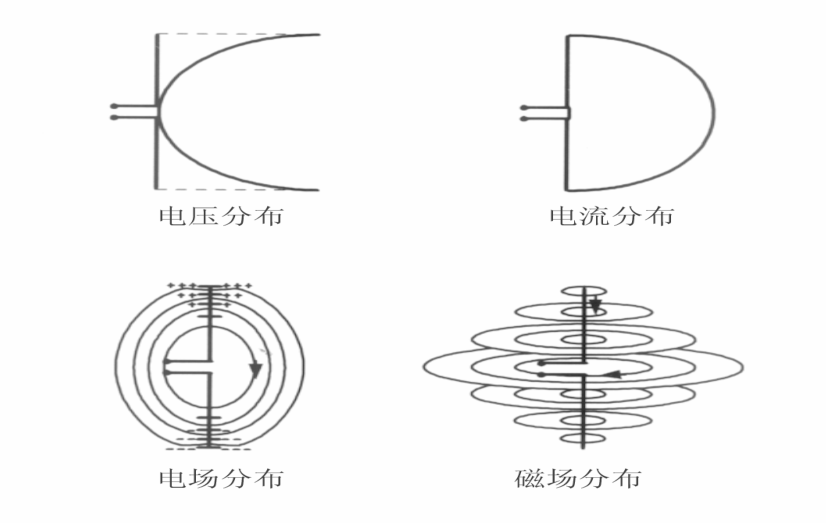
Antenna Input Impedance
🚧
References and Acknowledgments
- "Antennas - Radio Wave Learning Materials_Huawei"
- Antenna Gain, Mastering the First Lesson in Antennas
Original: https://wiki-power.com/ This post is protected by CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 agreement, should be reproduced with attribution.
This post is translated using ChatGPT, please feedback if any omissions.