Leakage Test
This post was originally written in English.
Leakage test contains input leakage test (IIL & IIH) and output tristate leakage test (IOZL & IOZH).
Input Leakage Test (IIL & IIH)
Input leakage occurs in a input pin's buffer circuit. IIH is the leakage path from input pin to GND when the DUT is driven to "1", and IIL is the leakage path from VDD to input pin when driven to "0":
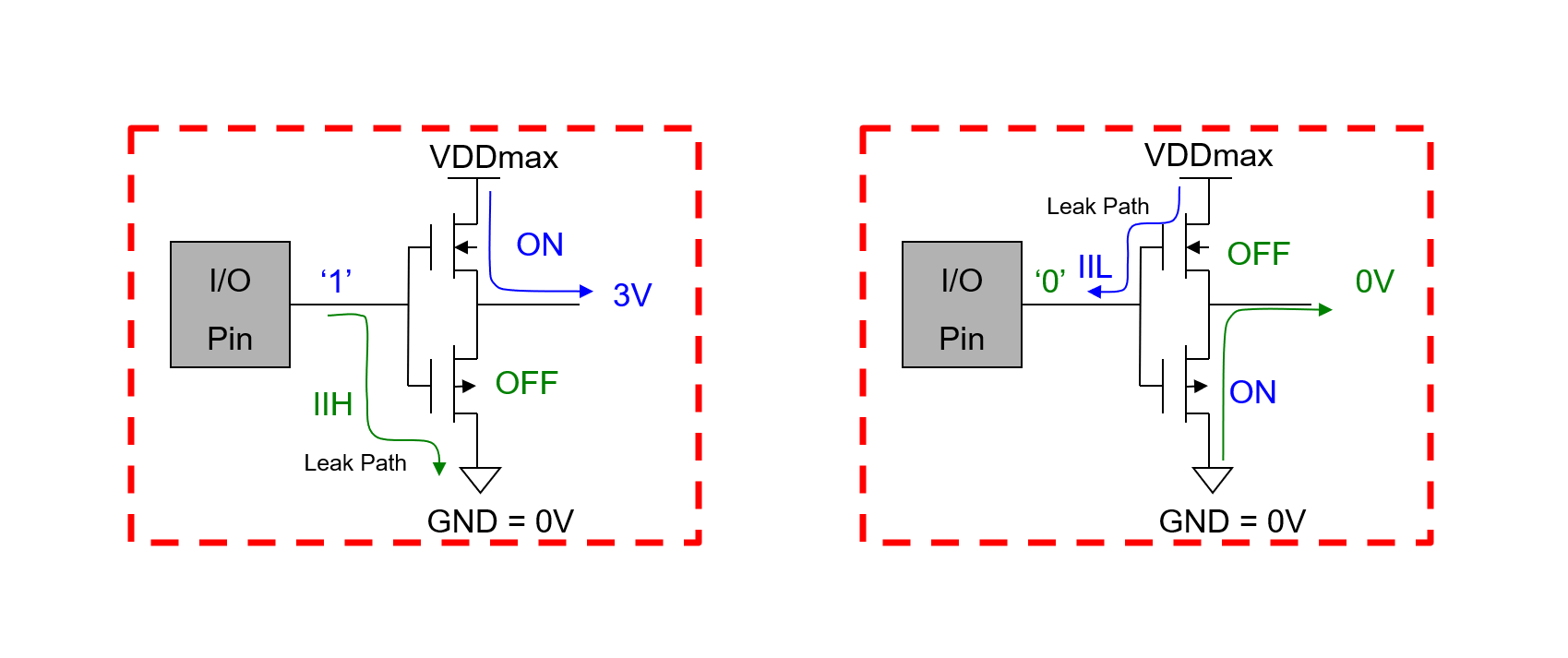
Actually, the measurement of IIL is the resistance from input pin to VDD, and IIH is the resistance from input pin to GND. Input leakage test is to ensure the pin's input buffer will not source or sink more unwanted current than specified.
Test Method (Serial)
Serial input leakage test (IIL & IIH) is performed with applying a voltage of VDDmax, and force the specific input pin to VDDmax (for IIH) or 0V (for IIL), while other input pins are forced to oppisite side of the Pin under Test.
IIL Test (Serial)
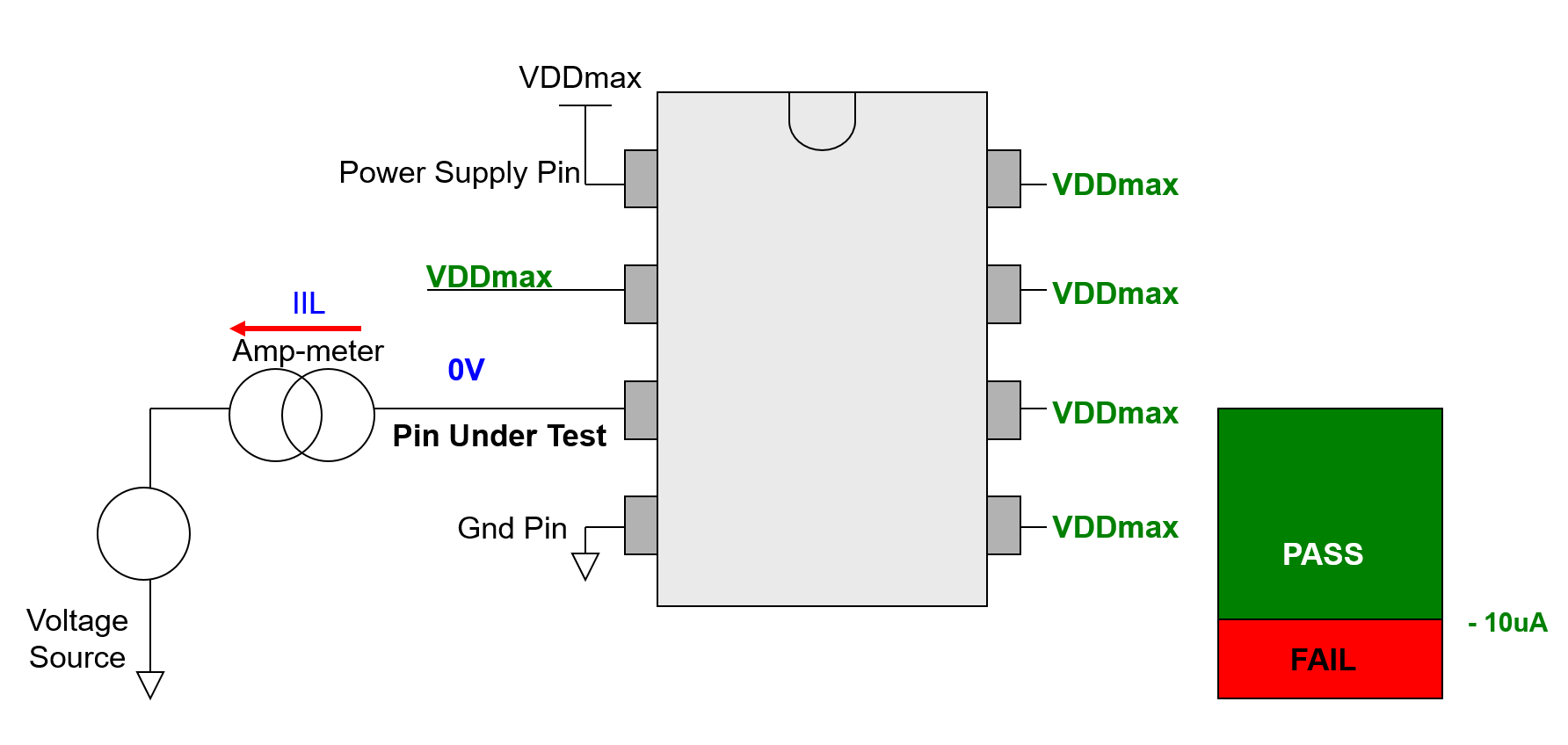
- Apply VDDmax to VDD pin (with current clamp).
- Force VDDmax to all input pins except for the Pin under Test.
- Force 0V to the Pin under Test, and measure the current flow out:
- Higher than spec value(>-10uA): PASS
- Lower than spec value(<-10uA): FAIL
- Repeat to test next pin.
IIH Test (Serial)
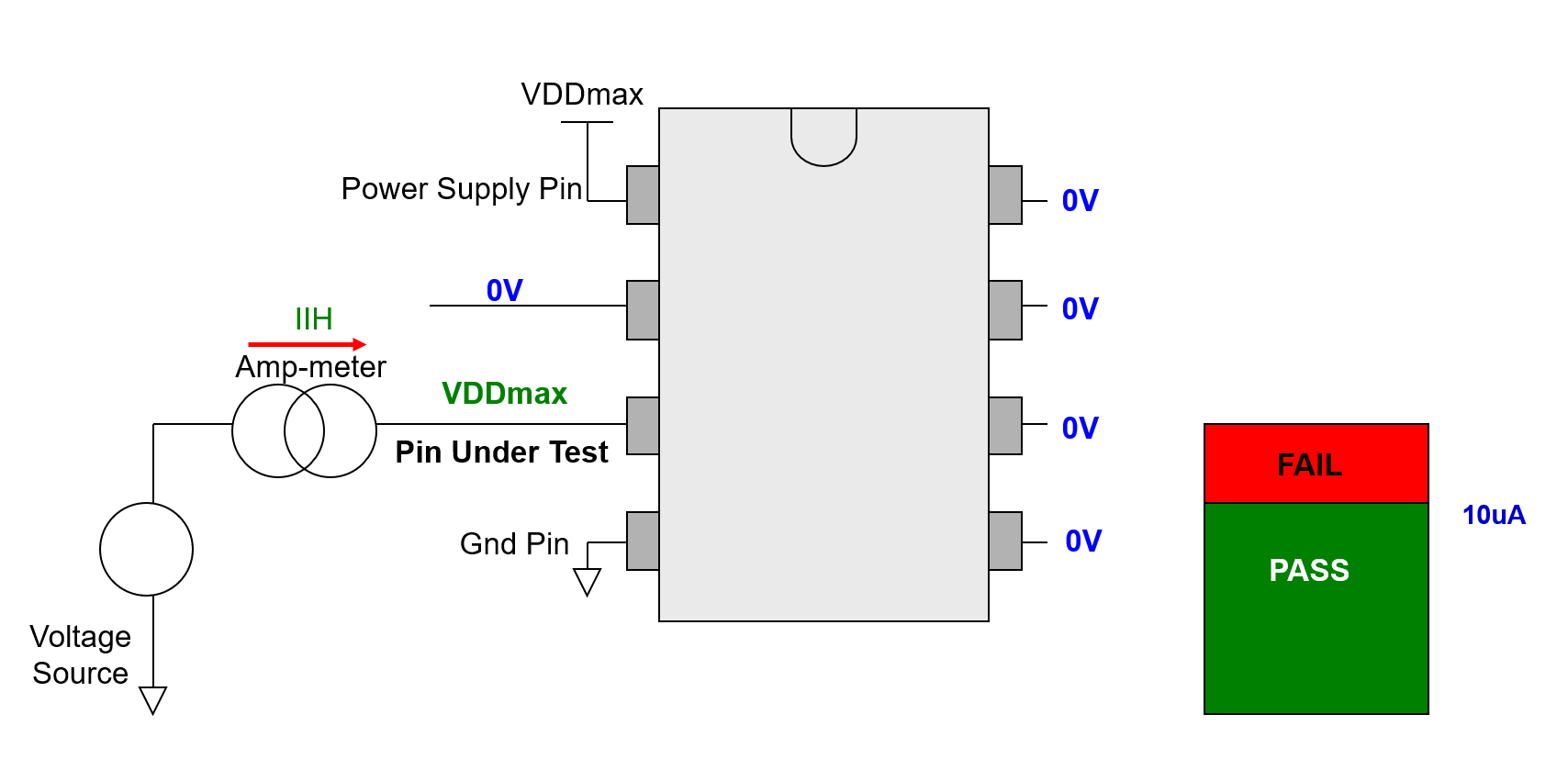
- Apply VDDmax to VDD pin (with current clamp).
- Force 0V to all input pins except for the Pin under Test.
- Force VDDmax to the Pin under Test, and measure the current flow into:
- Higher than spec value(>10uA): FAIL
- Lower than spec value(<10uA): PASS
- Repeat to test next pin.
Test Method (Parallel)
Since serial method can identify the leakage between input pins, but it's too inefficient. Parallel test method is more commonly used actually. PPMU is used in parallel method, to drive all input pins to VDDmax (for IIH) or 0V (for IIL) and measure the current of per input pin.
The only disadvantage of parallel method is pin to pin leakage will not be detected, because all the pins are forced to the same voltage level at the same time.
Output Tristate Leakage Test (IOZL & IOZH)
Tristate also named as High-Z or floating state, indicates appear to be high impedance externally of DUT's pin.
Output tristate leakage occurs in HIGH or LOW voltage level is applied on the DUT's output pin, while the pin is preconditioned to be disabled. IOZL means the current flow out when the LOW level is applied, and IOZH means the current flow into when the HIGH level is applied.
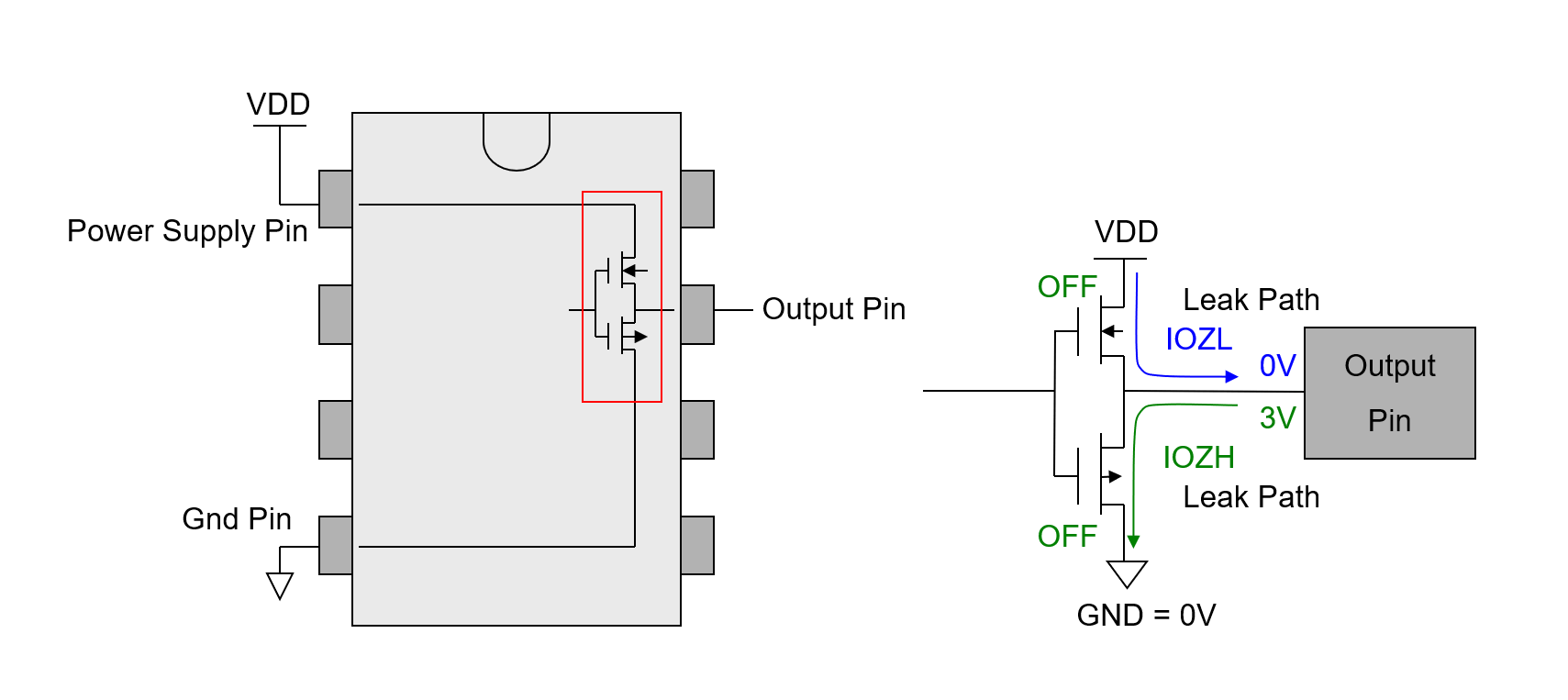
Essentially, IOZL indicates the resistance from an output pin to VDD when disabled, and IOZH indicates the resistance to GND. The test insures the pin will not source or sink more unwanted current than specified.
Additionally, a control input (enable signal) is required in this test , to controls the specific output pin to LOW, HIGH or High-Z (disable) state.
Test Method (Serial)
IOZL Test (Serial)
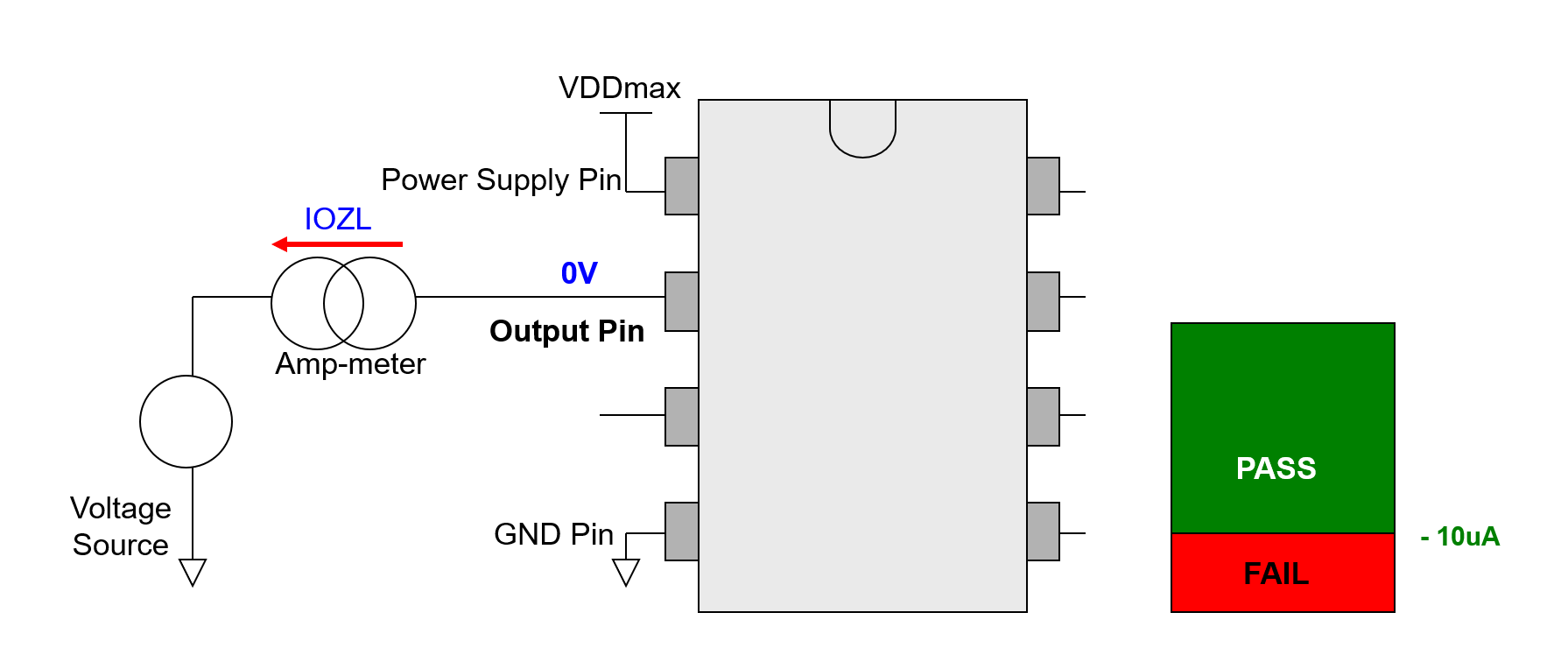
- Apply VDDmax to VDD pin (with current clamp).
- Precondition the specific out pin to Hi-Z (disable) state.
- Force 0V to the Pin under Test, and measure the current flow out:
- Higher than spec value(>-10uA): PASS
- Lower than spec value(<-10uA): FAIL
- Repeat to test next pin.
IOZH Test (Serial)
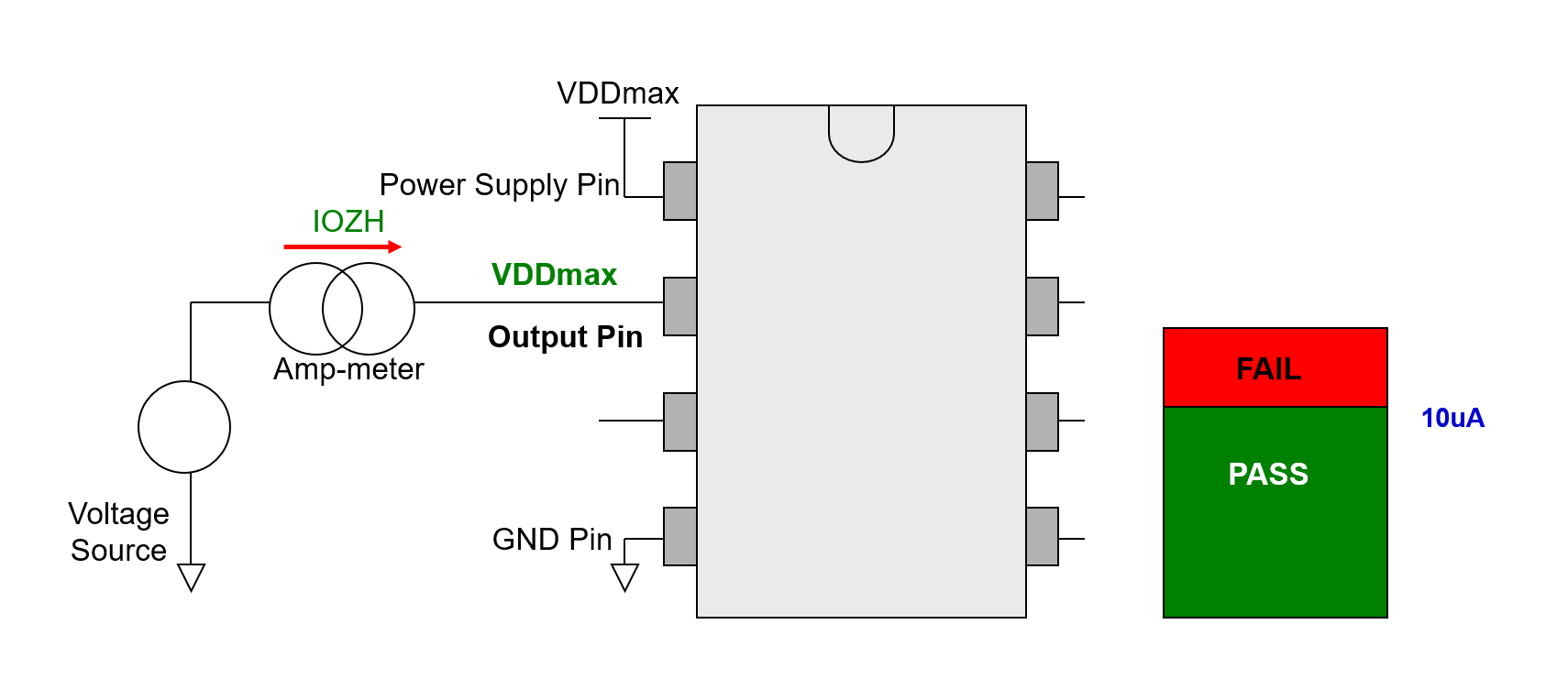
- Apply VDDmax to VDD pin (with current clamp).
- Precondition the specific out pin to Hi-Z (disable) state.
- Force VDDmax to the Pin under Test, and measure the current flow into:
- Higher than spec value(>10uA): FAIL
- Lower than spec value(<10uA): PASS
- Repeat to test next pin.
Test Method (Parallel)
Parallel method is more commonly used actually with PPMU, to drive all output pins to VDDmax (for IOZH) or 0V (for IOZL) and measure the current of per output pin.
References & Acknowledgements
- The Fundamentals Of Digital Semiconductor Testing
- Fundamentals of Testing Using ATE
Original: https://wiki-power.com/
This post is protected by CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 agreement, should be reproduced with attribution.