Basics of Mixed Signal Test
This post was originally written in English.
Mixed signal contains both analog and digital signals. Devices processing mixed signal typically include ADCs, DACs, analog switches and multiplexers, sample-and-hold amplifiers, and so on.
As a part of it, analog signals is signals we use in the real world such as voice or tempurature, it's continuous in both time and amplitude. To process analog signals into computers, we need to convert them to digital signals, as it's discrete in both time and amplitude.
Sampling Theory
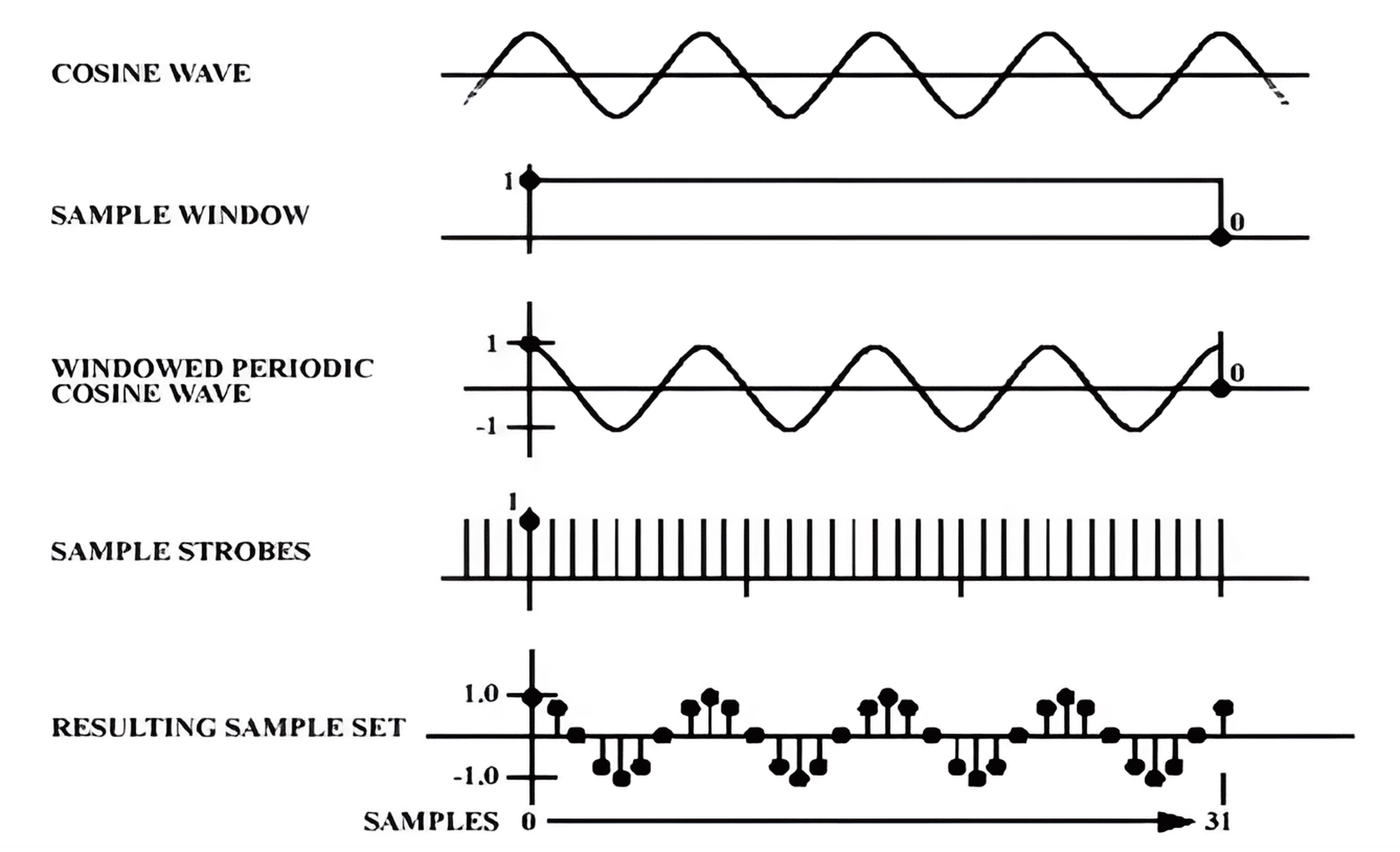
Sampling theory applies to the signal to be periodic, or errors will be introduced.
Nyquist Theorem
We use Nyquist Theorem(奈奎斯特定理) to gain the minimum sampling frequency when sampling signals:
We must sample at a rate higher than twice the highest frequency of interest, to be able to recreate a signal from its samples and avoid losing information.
If we sample at a frequency that lower that the Nyquist rate, it will exhibit a phenomenon called aliasing(混叠)(unwanted components) when we try to convert it back to a continuous time signal, and some of the frequencies in the original signal may be lost.
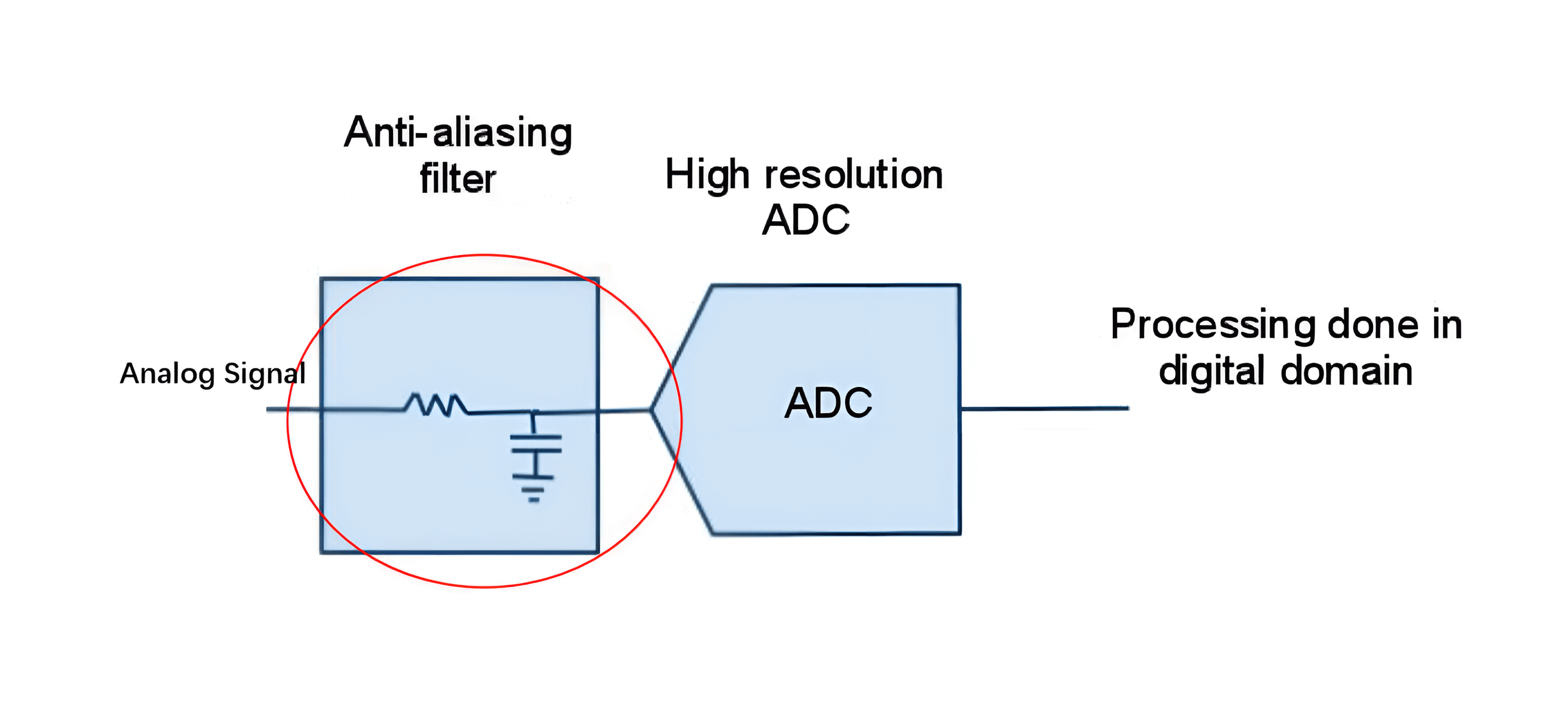
To minimize aliasing problem, we need to remove the frequency greater than \(\frac{F_s}{2}\) of the signal, via the anti-aliasing filter (e.g. low-pass-filter):
Coherent Sampling
If a time sample set does not contain a precise integer number of cycles, spectral leakage(频谱泄露) will occur.
Coherent sampling(相干采样) is to ensure the continuity of sampling and prevent spectral leakage, it guarantees that a sample set (a series of samples which represent the analog signal) has a fixed and well defined relationship between the sample frequency \(F_s\), the number of samples \(N\), the test signal frequency \(F_i\), and the number of test signal periods sampled \(M\):
The total time required to take all samples is called the Unit Test Period (UTP) and requires \(M\) cycles of the test signal, which has frequency \(F_i\).
For an example, if we want to calculate the \(F_s\) of continuous repeating sinewave, where \(F_i\) is 1kHz, \(M=3\) and \(N=16\):
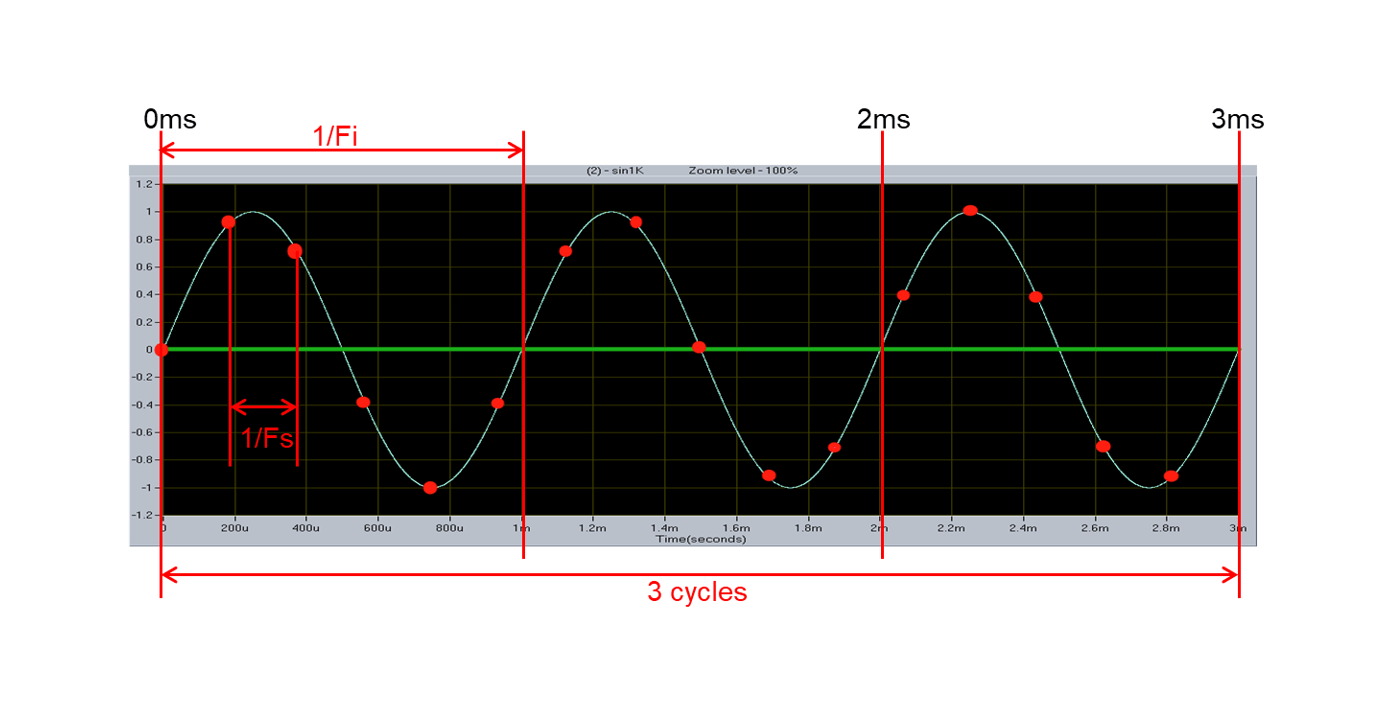
So we can conclude that \(F_s=5.333kHz\).
Important tips of coherent sampling:
- Increasing \(M\) and/or \(N\) will increase both accuracy and test time.
- \(M\) and \(N\) needs to be an integer.
- \(N\) needs to be a power of 2 when using Fast Fourier Transform (FFT).
- \(M\) and \(N\) are recommended to be mutually prime(互质)so that each sample gives unique information. Described in the following.
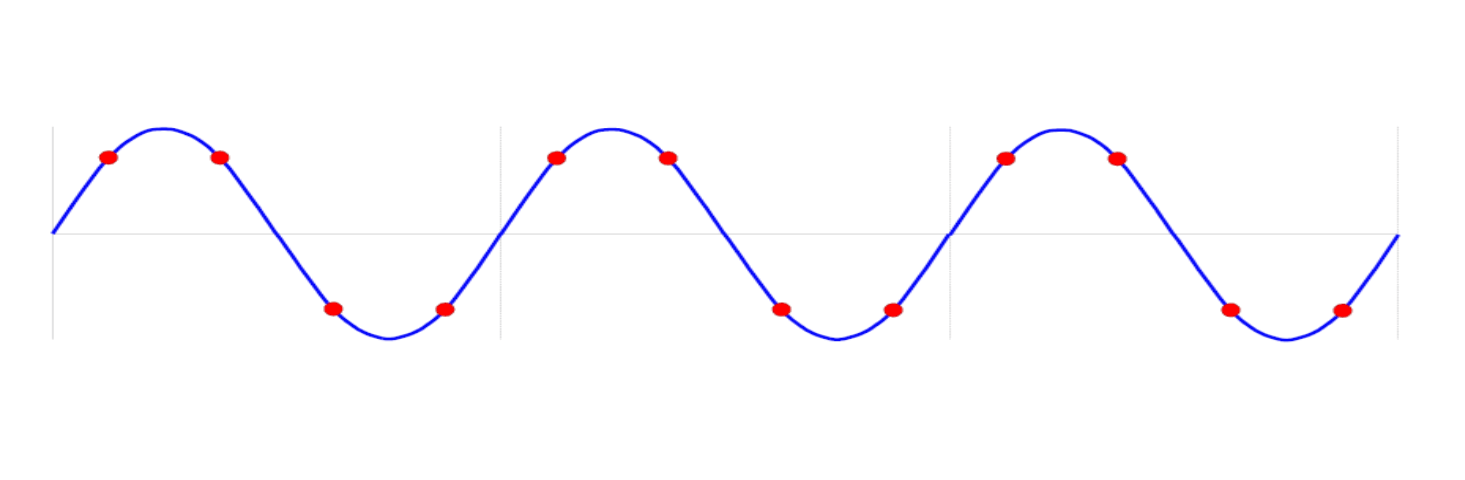
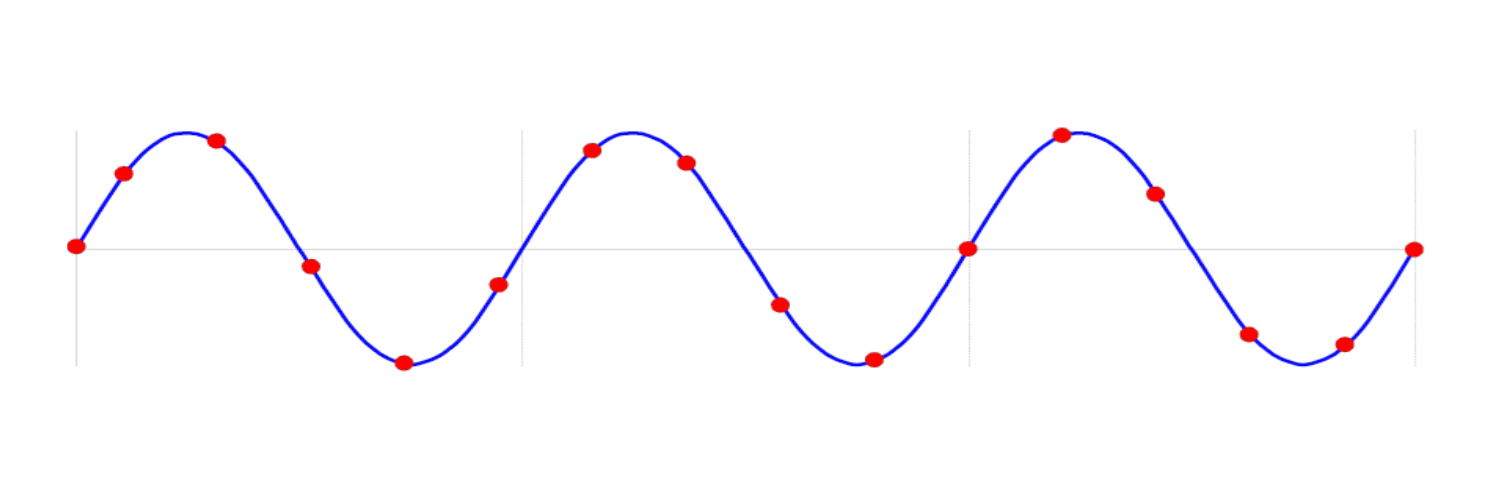
If \(M\) and \(N\) are not mutually prime (\(M=3,N=12\)), samples are taken at the same position in every cycle, so there is no new information:
If \(M\) and \(N\) aremutually prime (\(M=3,N=16\)), so they are mutually prime and every sample is discrete, so it gives unique information:
Common Frequency Analysis Algorithms
For \(N\) time-domain signal samples, there are \(N\) frequency-domain signal values, and there are \(N/2\) frequency-domain power spectrum values. A typical spectral components example is shown below:
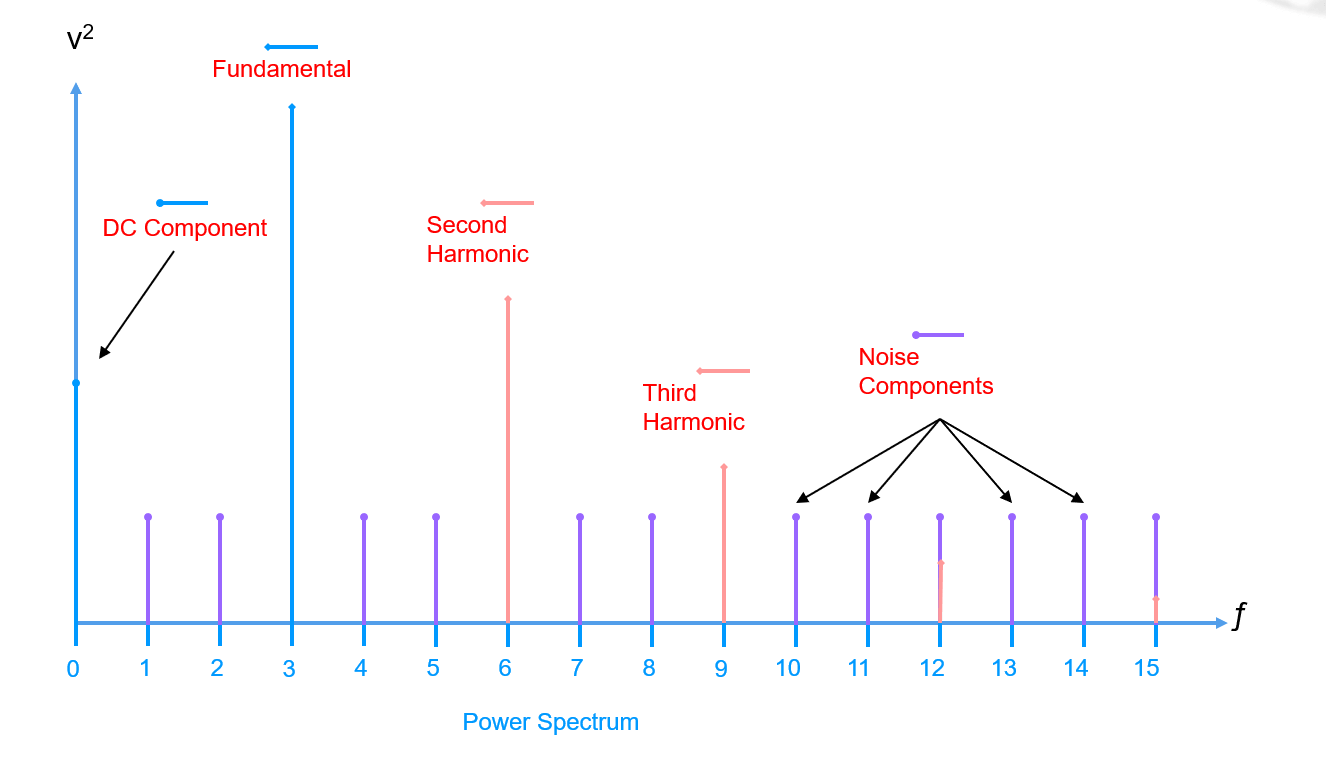
There are several parameters for describing spectral components as follows:
- Signal To Noise Ratio (SNR)(信噪比)
- Total Harmonic Distortion (THD)(总谐波失真)
- Signal to Noise and Distortion (SINAD)(信纳比)
- Intermodulation Distortion (IM)(互调失真)
- Spurious Free Dynamic Range (SFDR)(无杂散动态范围)
Signal To Noise Ratio (SNR)
Signal To Noise Ratio (SNR) is derived by storing the value of the fundamental (signal power) first:
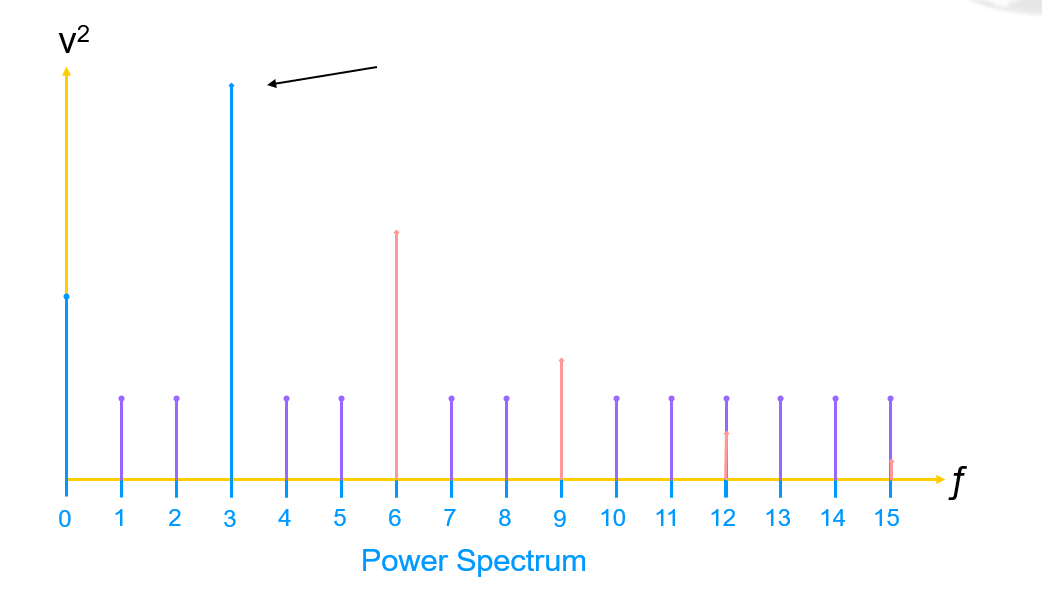
Then remove the DC component and harmonics (usually up to 5):
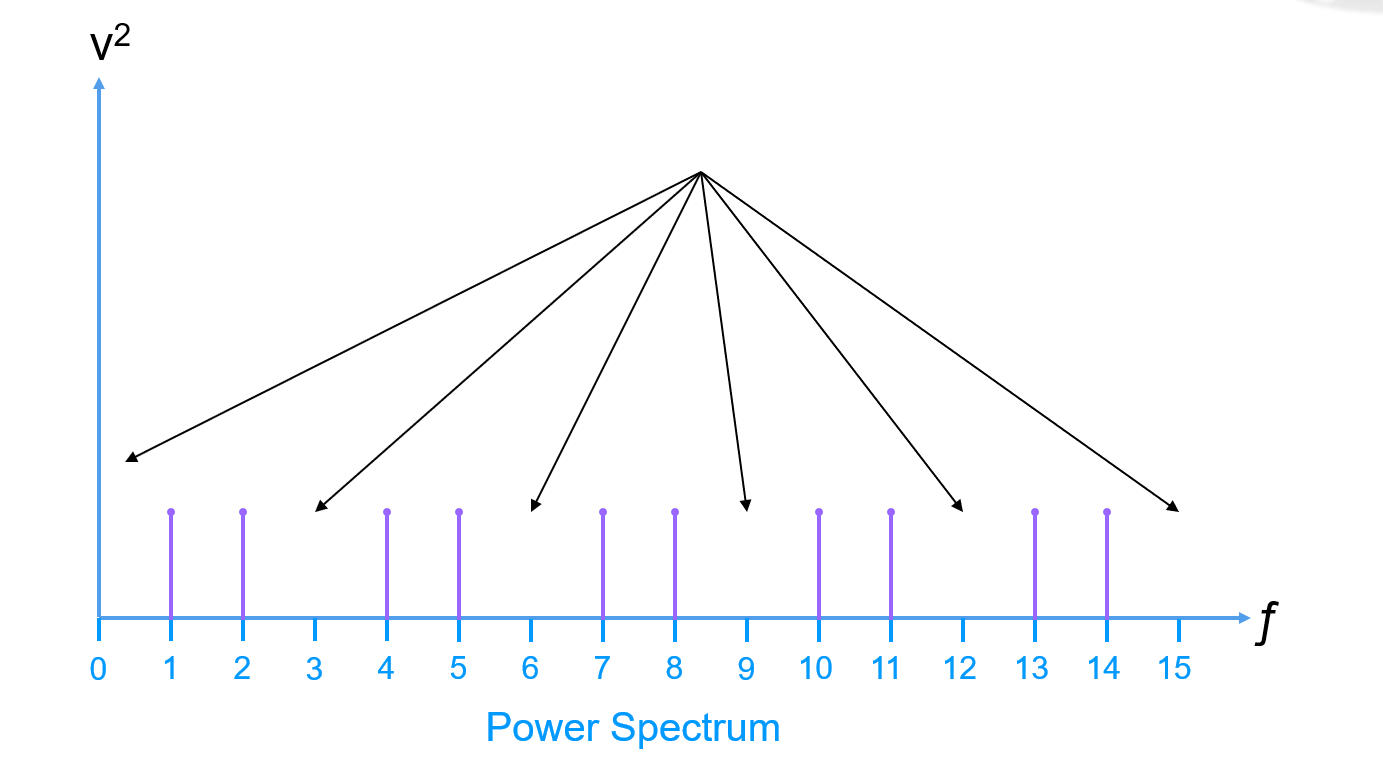
Next sum all bins of the remaining power spectrum (the noise power) measured by the RMS value (Root Mean Squared, The analog voltage that is equal to a DC voltage containing the same amount of energy, for a sine wave, the RMS value is 0.707 times the peak value):
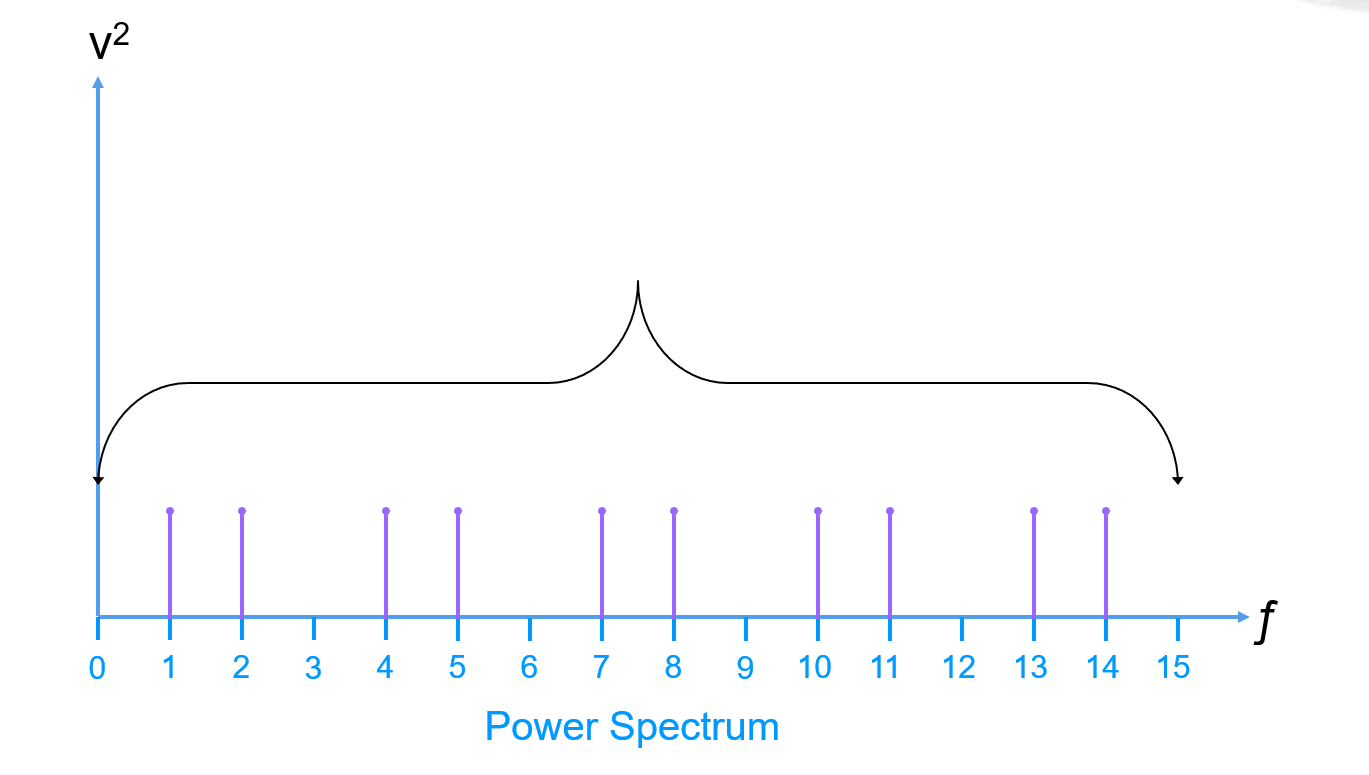
Ultimately we can conclude that:
SNR is usually expressed in decibels (dB), and is often a positive value (assuming the Fundamental Power is much larger than the Noise Power).
Total Harmonic Distortion (THD)
Total Harmonic Distortion (THD) is derived by keeping a running sum of the total harmonic power (usually only the first five harmonics, start at the second harmonic):
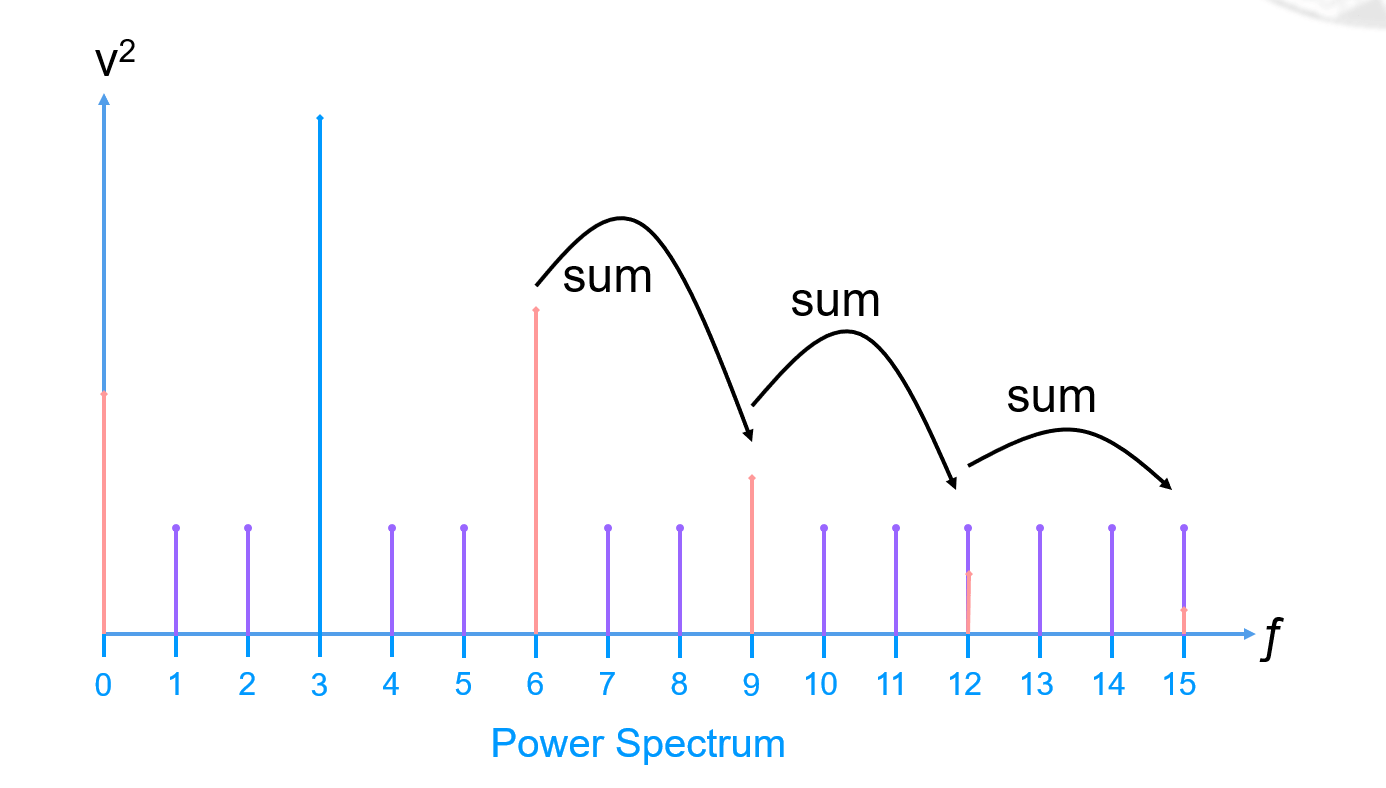
And we can conclude that:
THD is often a negative value (assuming the Fundamental Power is much larger than the total Harmonic Power).
Signal to Noise and Distortion (SINAD)
Signal to Noise and Distortion (SINAD) is the same methodology as computing SNR, but now the power of the harmonics is added into, and only zero out the DC component.
And we can conclued that:
Intermodulation Distortion (IM)
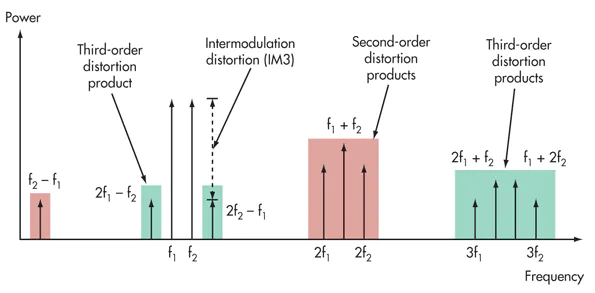
Intermodulation Distortion (IM) occurs when two or more signals are used in a non-linear system. The spectrum will not only consist of the original signals, but will also contain the sum and difference of the input signals along with their harmonics.
Spurious Free Dynamic Range (SFRD)
Spurious Free Dynamic Range (SFRD) is derived by finding the highest element after the fundamental (ignoring the DC component):
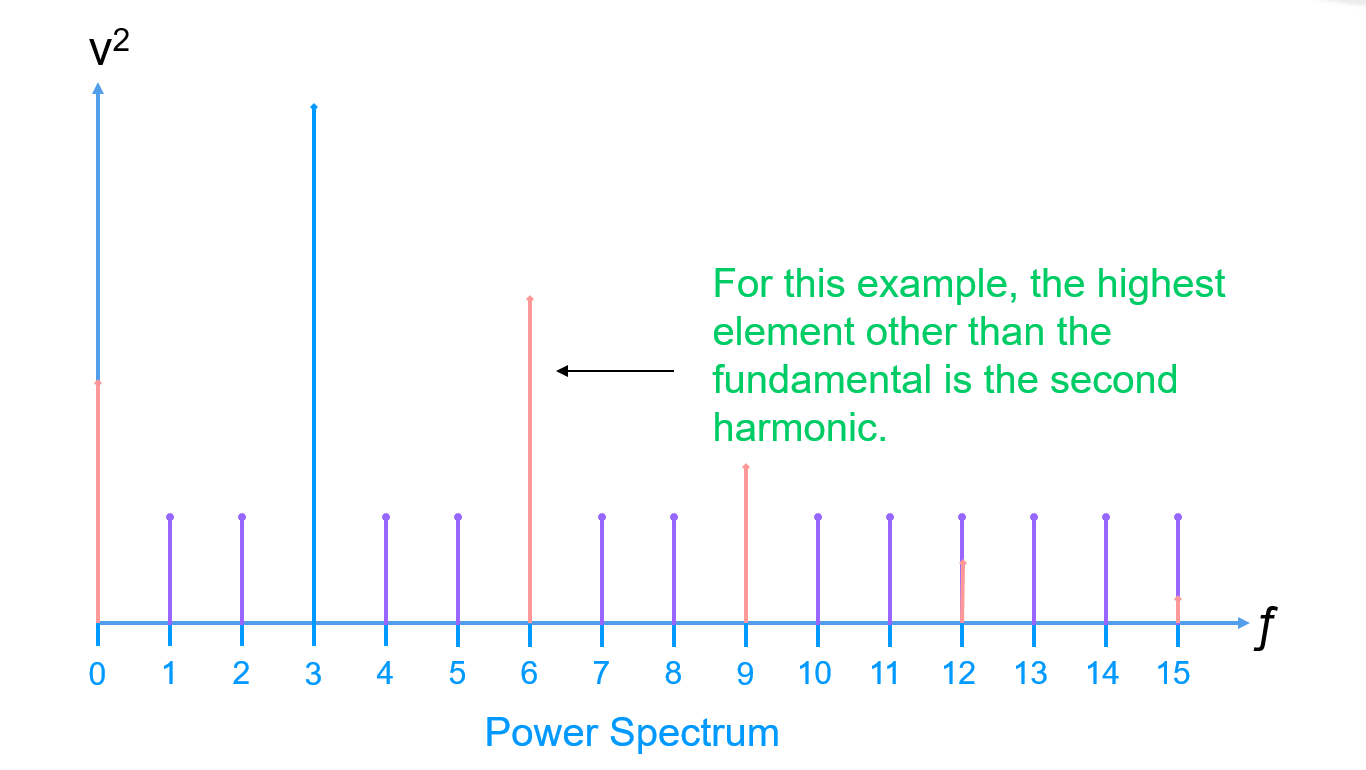
Note that the highest element may or may not be a harmonic. So we can conclude that:
The Spurious Free Dynamic Range is a positive value (assuming the Fundamental Power is much larger than the next highest Spur Power.
Architecture of Generic Mixed Signal Tester
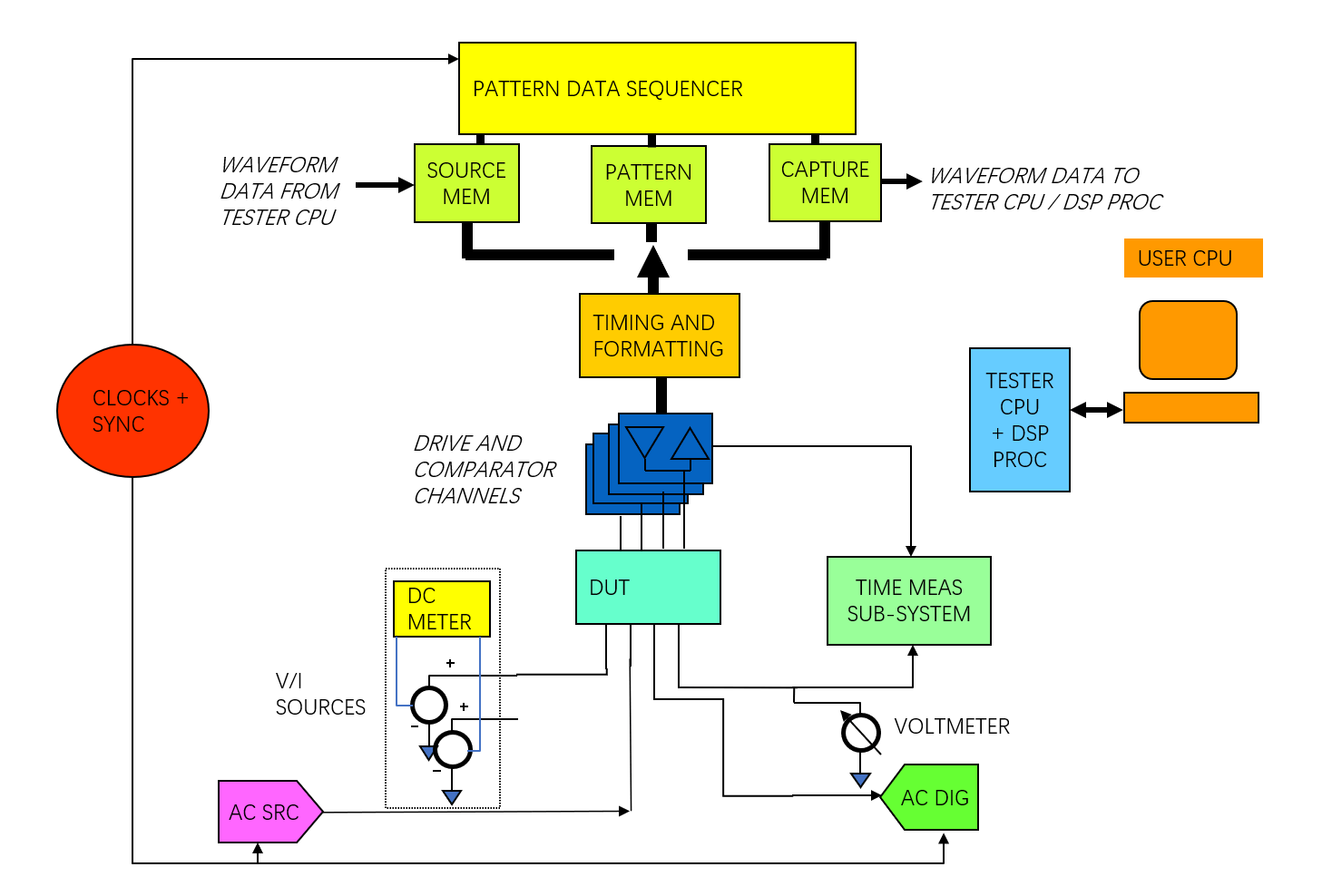
In the generic mixed signal tester, the AWG (AC src) and WD (AC dig) are both connected to the DUT via relay interconnects through the channel board.
Arbitrary Waveform Generator (AWG)
Arbitrary Waveform Generator (AWG) is a low distortion signal generator. It contains a DAC to generate an analog signal from the digital data.
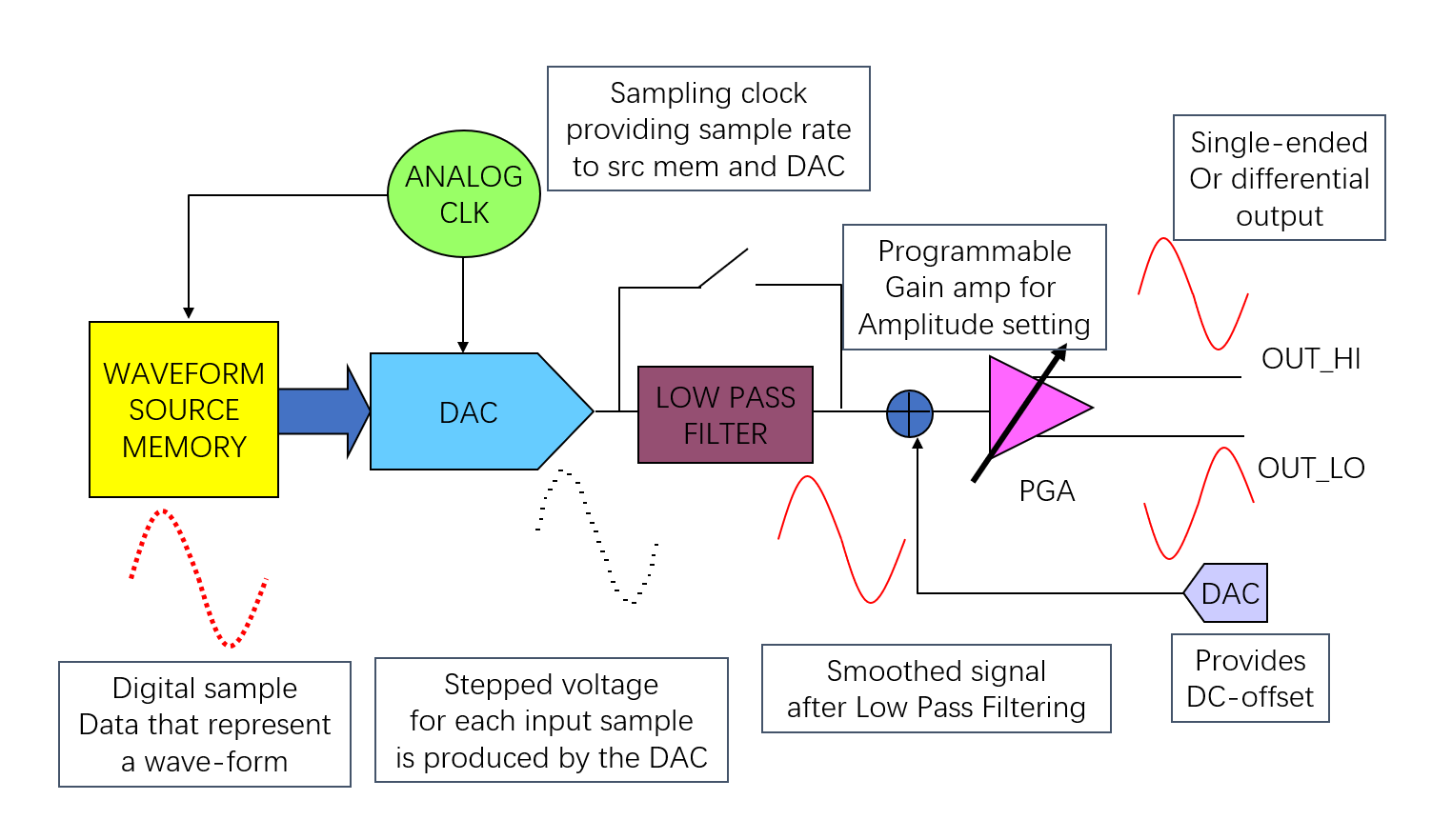
LPF (Low Pass Filter) is to smooth the waveform and remove high frequency components. A set of data points for a given waveshape is stored in the waveform source memory, each time a clock occurs, a data point will pass to the DAC.
Important parameters of AWG:
- Maximum Peak to Peak Voltage output
- Waveform resolution (DAC resolution)
- Band-width
- Waveform source memory depth
- Output Impedance
- Noise, THD, SNR
Waveform Digitizer (WD)
Waveform Digitizer (WD) samples analog signals, and converts them into digital values. It performs the opposite operation to the AWG. It converts analog signal into digital samples that represent the original analog signal.
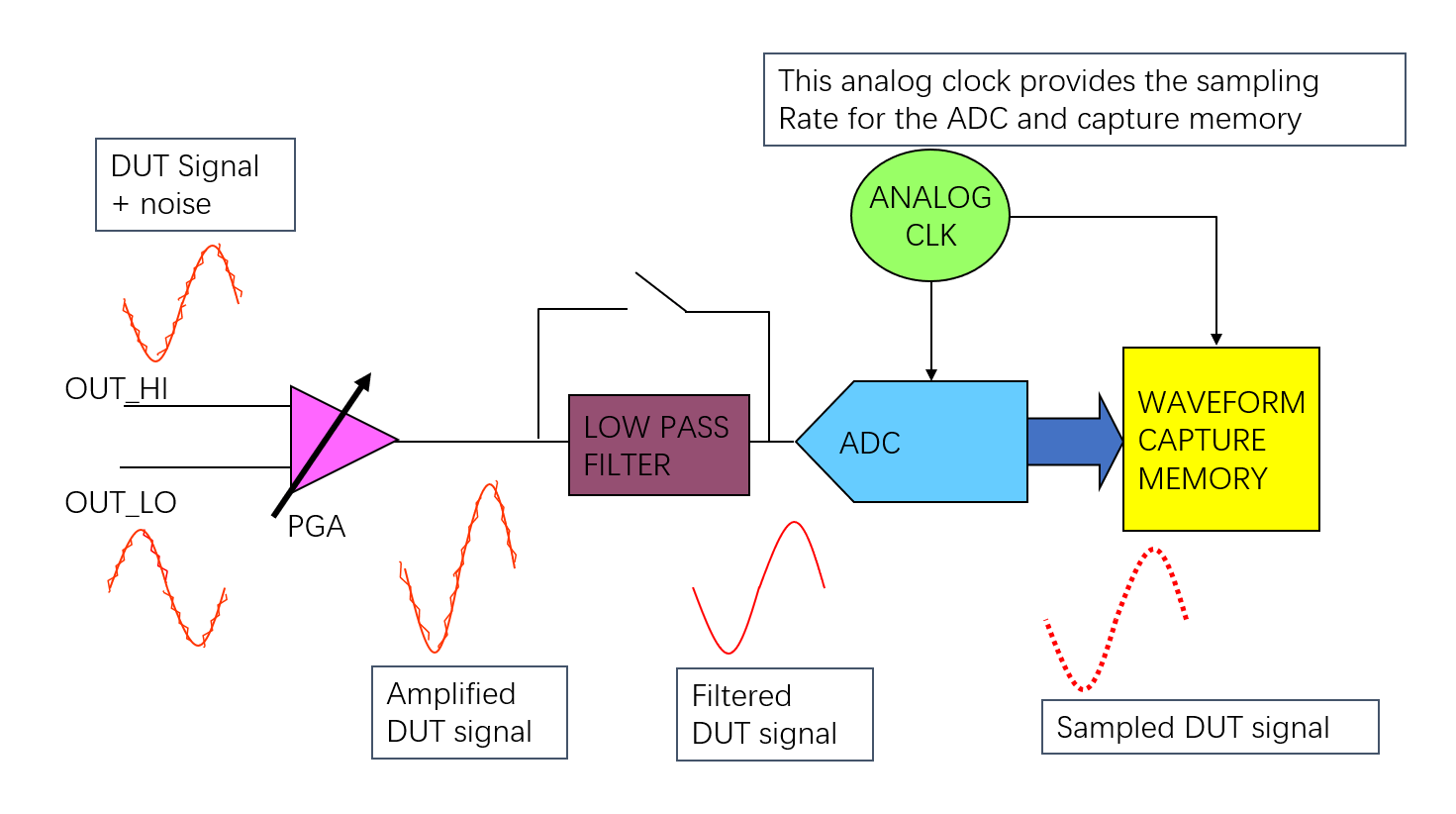
The low-pass filter limits the bandwidth of the signal in order to remove unwanted frequency components like noise and spurs, also provides anti-aliasing by attenuating spurs that would be aliased into the pass band of the filter during the ADC conversion.
Important parameters of WD:
- Maximum Peak to Peak input Voltage range
- Waveform resolution (ADC resolution)
- Band-width
- Waveform capture memory depth
- Input Impedance
- Noise, THD, SNR, spur
Clock
The analog and digital clocks are derived from a system wide reference clock. If there is no clock synchronization signal, the timing offset may lead to incorrect results.
Digital Signal Processor (DSP)
Digital Signal Processor (DSP) is a specialized microprocessor to performs mathematical operations on arrays of digital numbers. Various algorithms like DFT and FFT are performed on DSP to transform time domain information into the frequency domain.
The architecture of a DSP is optimized to allow fast multiplication, summing, logarithm calculations, squaring, and square root calculations.
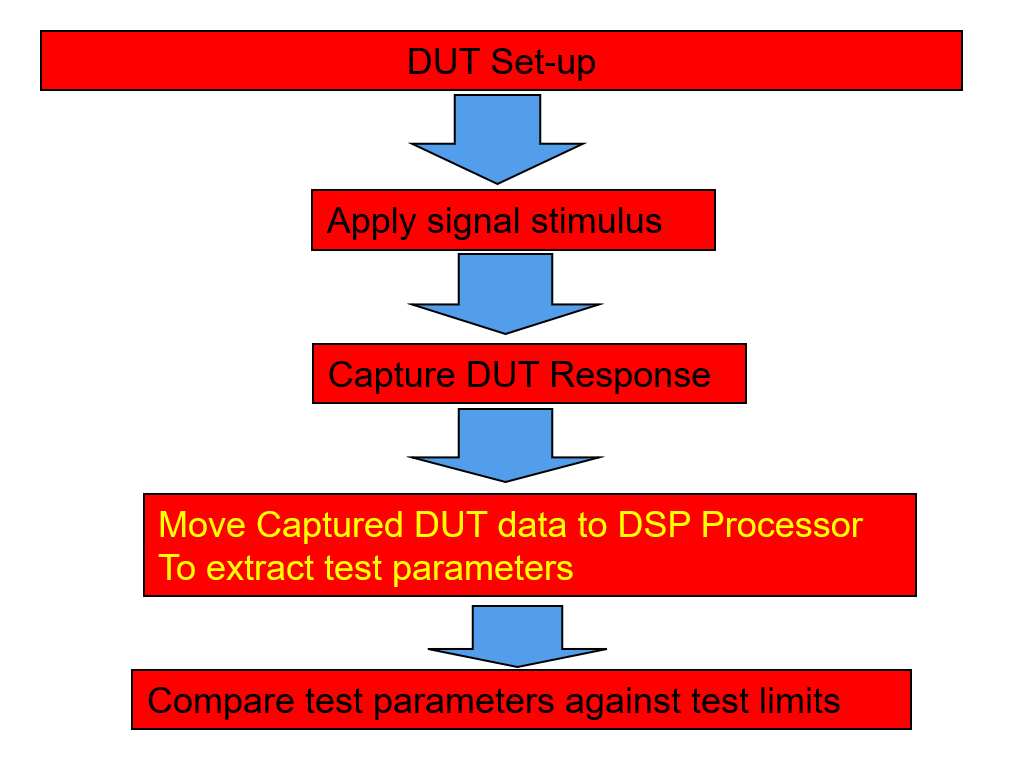
The tester will carry the stored captured signal to the DSP processor through data buses.
References & Acknowledgements
- Fundamentals of Testing Using ATE
- The-Fundamentals-of-Mixed-Signal-Testing_Brian-Lowe
Original: https://wiki-power.com/
This post is protected by CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 agreement, should be reproduced with attribution.